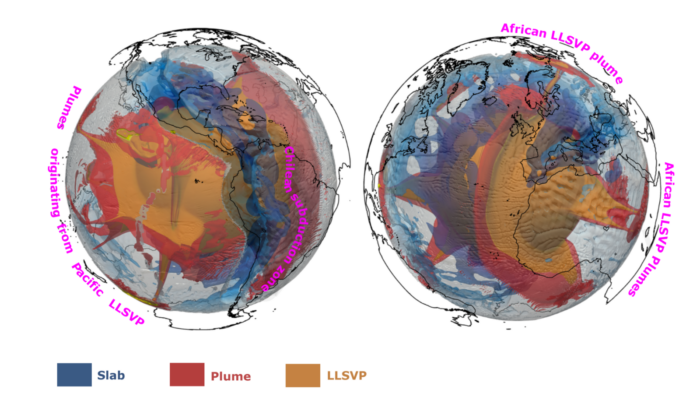
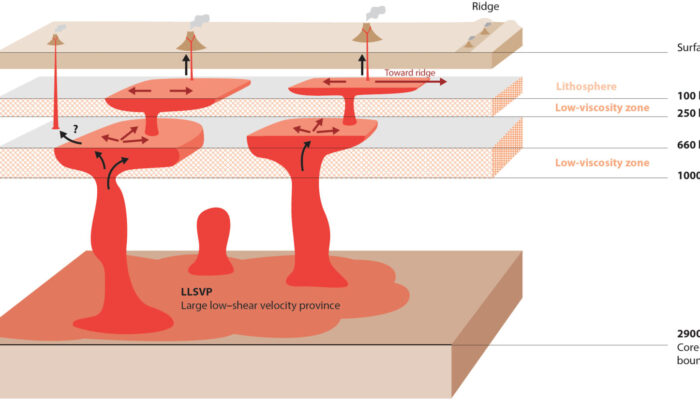
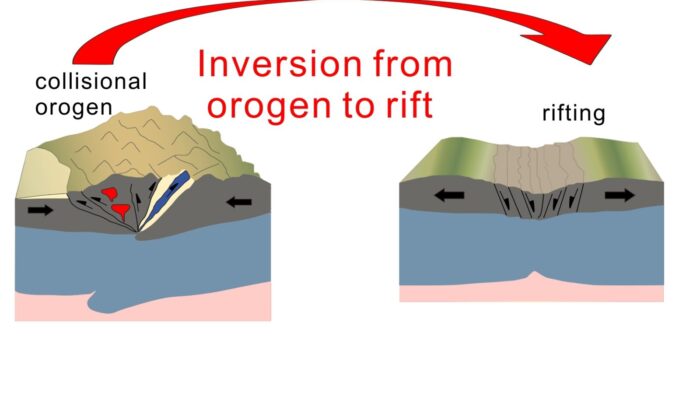
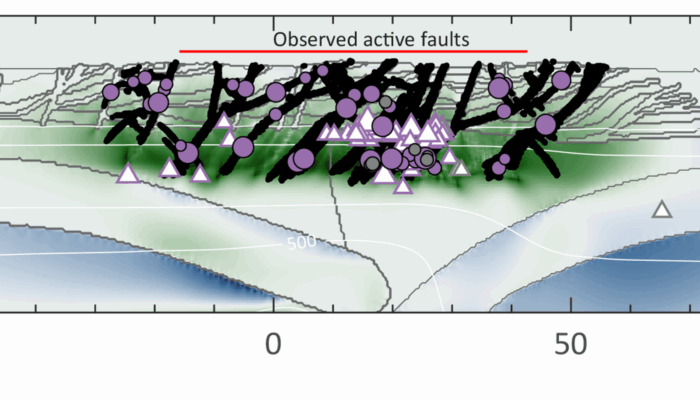
Seismic waves tell us that something unusual is happening in the lowermost few hundred kilometers of Earth’s mantle. Beneath Africa and the Pacific lie two enormous thermochemical structures known as Large Low-Shear-Velocity Provinces (LLSVPs). These “large blobs” are slower to transmit shear waves, but beyond that, their physical nature remains one of the biggest open questions in deep Earth geod ...[Read More]
What’s blobbing inside the Earth? – insights from numerical modelling