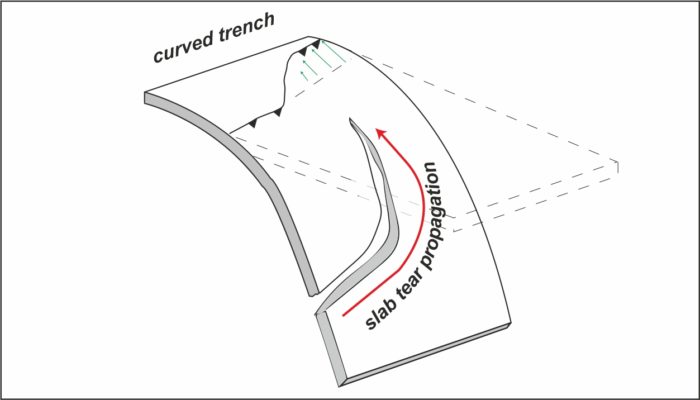
Slab tearing refers to the gradual propagation of the break-off of a subducting plate. As observed in numerous modern and ancient convergent tectonic settings, the growth of the tear “window” in the downgoing plate has strongly influenced various geologic and geodynamic processes, such as depocenter migration of foreland basins, uplift rates in mountain ranges, earthquakes, volcanism, and flow pat ...[Read More]
The first observational evidence for a volcanically active Venus
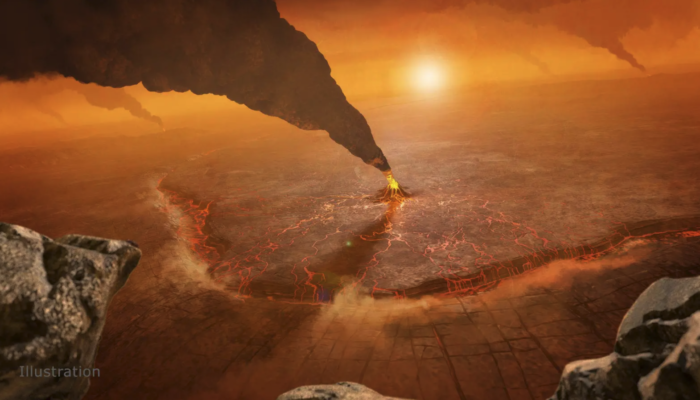

Our neighbouring planet Venus is gaining popularity in the terrestrial planetary sciences, especially since the selection of three new Venus missions by NASA and ESA in 2021. Now, for the first time ever, scientists have directly observed surface changes that indicate active volcanism on Venus. This discovery was made with data from NASA’s 30-year-old Magellan mission and is only a small preview f ...[Read More]
Geodynamics 101 – Viscous anisotropy
We are living in an anisotropic world. From rock-building crystals, ice, and trees growing in your garden to your favourite slice of cake many materials or objects has some anisotropic behaviour. What does this mean? Anisotropy (non-isotropy) implies that a material property depends on the direction of the measurement. In geodynamics we often talk about seismic anisotropy, originating from microsc ...[Read More]
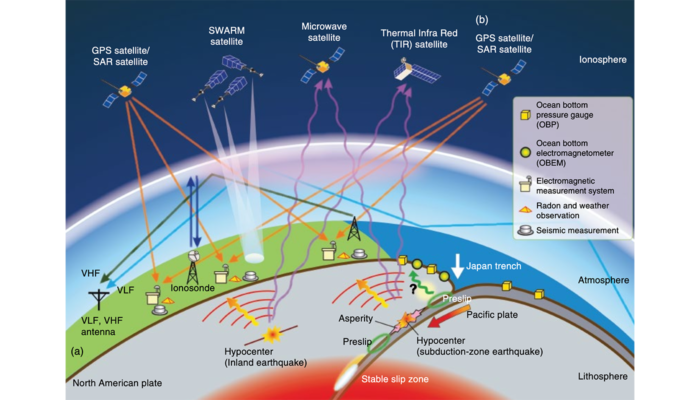
Study of the Lithospheric deformations, Earthquakes, Tsunamis, Volcanic eruptions and their imprints in Atmosphere using Space Geodetic Observations
The fundamental of Space Geodesy is the observation of the dynamics of the Earth, such as its rotation on its axis, changes in shape, and the external gravitational field etc., which allow for the monitoring of the Earth system in general. Space Geodetic techniques, such as Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) / Global Positioning System (GPS), as well as Interferometric Synthetic Aperture R ...[Read More]