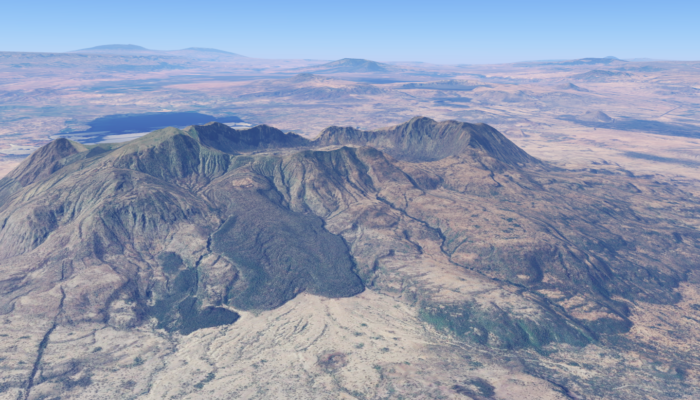
Building the Earth in a sandbox The Main Ethiopian Rift stretches for hundreds of kilometers through Ethiopia, a massive fracture where Africa is slowly tearing apart to birth a new ocean. However, the processes driving this continental breakup remain hidden deep beneath layers of volcanic rock and millions of years of geological history. Today, in a laboratory in the heart of the be ...[Read More]
Unraveling volcanic patterns between adjacent rift zones
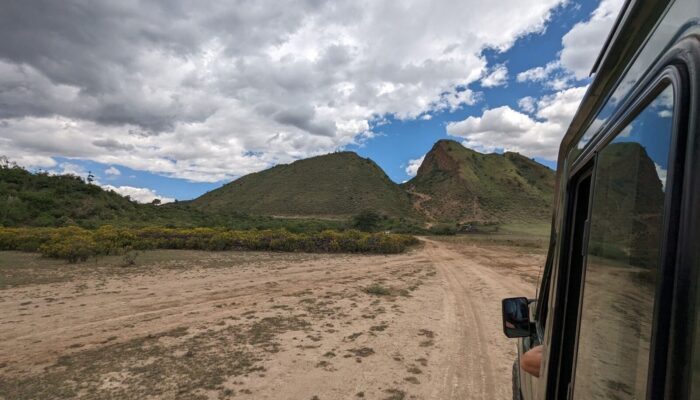

Continental rifts are a prime example of how the forces at work beneath our feet are constantly shaping our world, and often host volcanic activity. The patterns and distribution of volcanism in rift settings, however, is far from intuitive. The picture gets even more complicated if we look between the segments that often make up a rift. This week, Valentina Armeni from the University of Potsdam, ...[Read More]
Coexisting Forces in Geodynamic Modelling: Pros, Cons, and Synergies of Analogue and Numerical Modelling
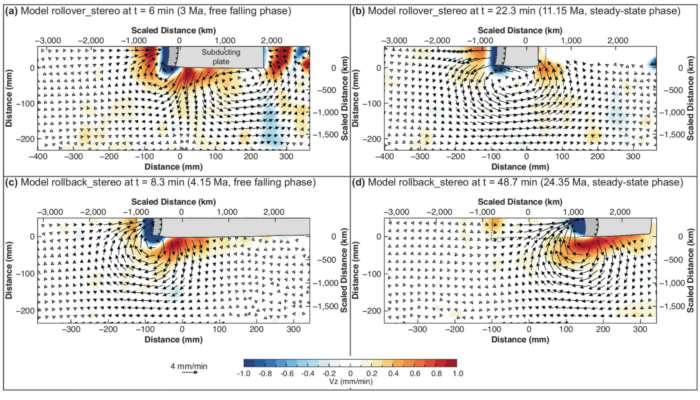
Geodynamic modelling helps us understand Earth’s internal processes by providing a framework to test hypotheses. Analogue modelling uses physical models governed by the laws of nature, with resolution down to Planck’s length. In contrast, numerical modelling employs mathematical methods to approximate solutions to the physical laws governing Earth’s processes. Each modelling approach comes with it ...[Read More]
A voyage between different tectonic modelling worlds: from sandbox to supercomputer
A voyage between different tectonic modelling worlds: from sandbox to supercomputer


