The Earth’s internal engine drives several geodynamic processes such as continental rifting and dynamic topography, shaping mesmerizing landscapes. Through numerical modeling, insights into formations like the Continental Rift of Southeastern Brazil deepen our appreciation of Earth’s dynamic nature and the forces sculpting its surface. The heat engine beneath our feet Not so long ago, ...[Read More]
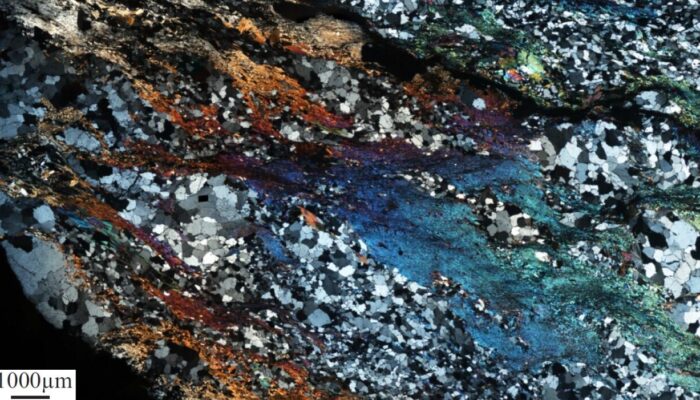
Exploring rheology of Earth’s materials: The marvels of high-temperature high-pressure deformation experiments
The Earth, with its towering mountains, shifting tectonic plates, and dynamic geological processes, has always been a subject of fascination and inquiry for scientists. Amidst the vast array of scientific disciplines, one relatively small yet impactful field, known as experimental rock deformation, plays a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries hidden beneath the Earth’s surface. Though th ...[Read More]
Animating the past using numerical modeling
The human lifespan is too short compared to the geological time. To comprehend long-term phenomena, numerical modeling emerges as an imperative approach. But, there are several ways for visualizing the output of these models. Among these, animations stand out as a powerful tool, allowing us to watch the dynamic evolution of our planet over geological epochs like a movie. Our lives are too short co ...[Read More]
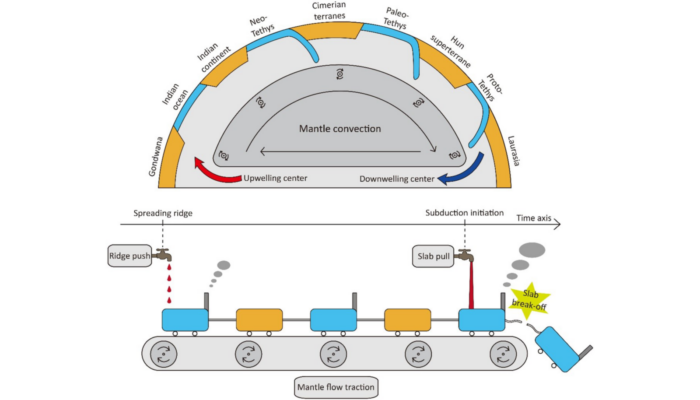
Multiengine-driving Tethyan evolution
The highest mountain range in the Alps in the Western Europe, the towering peaks of the Himalayas in Asia, and ~1/3 world crude oil production in the middle east – what brings these remarkable nature gift together? The answer is Tethyan orogenic belt, which spans across the entire Eurasian continent. This week, we are privileged to have Prof. Zhong-Hai Li from the University of Chinese Academy of ...[Read More]