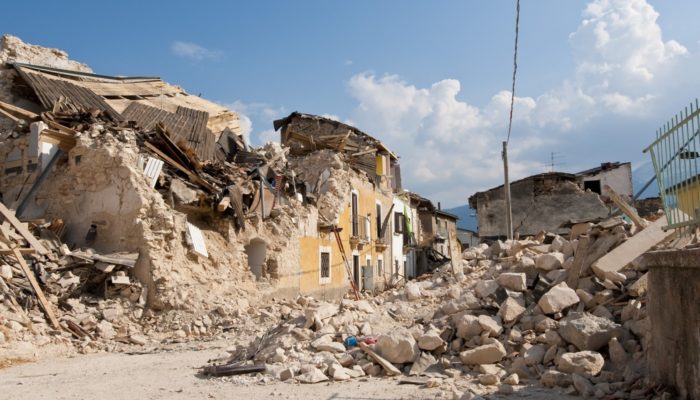
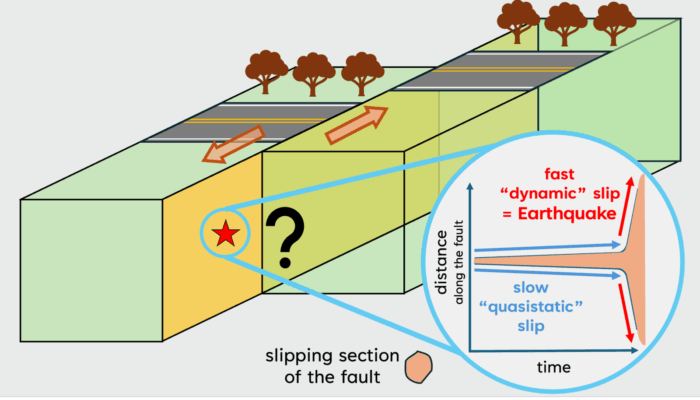
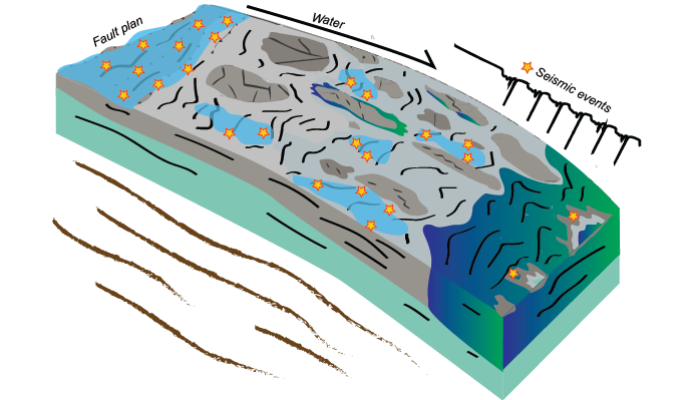
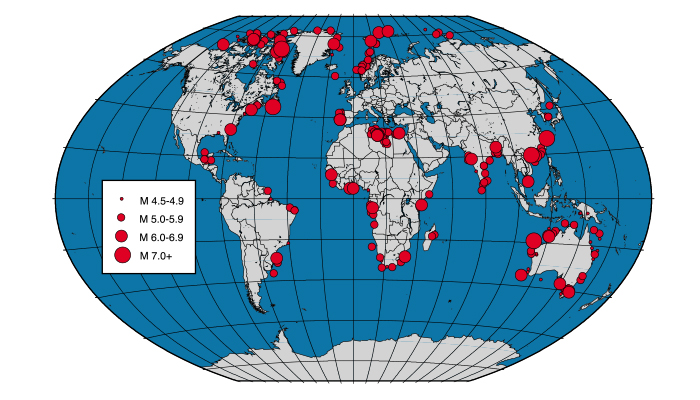
How do earthquakes start? Earthquakes occur when a block of rock rapidly slides past another along an interface or a discontinuity in the medium and release energy in the form of seismic waves. Turns out, the surface of the earth is riddled with a lot of these discontinuities, which we call “faults”. If we plot the locations of earthquakes on a world map (Figure 1a), we will see that they highligh ...[Read More]
Don’t Stop Me Now: A Fracture Mechanics Perspective on Earthquake Nucleation