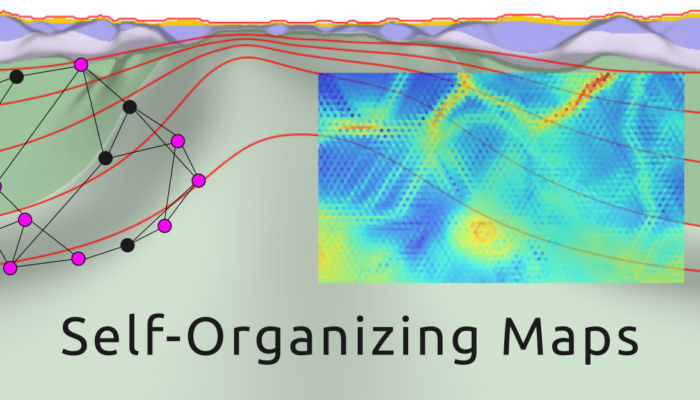
The huge amount of data produced in Geosciences is increasing exponentially, and numerical modelling has become a key tool for understanding tectonic evolution over time, which also increases the volume of data produced. Here, I, João Bueno (PhD student at University of São Paulo, Brazil) will present how a machine learning technique known as Self-Organising Maps can be used to understand the int ...[Read More]
Mathematical closed-form solutions in Geodynamics: insightful or detrimental?
Mathematics is certainly not every scientist’s cup of tea. Despite the latter, they are, for the most part, very important, since most problems, regardless of their complexity, start and end with a mathematical equation (or set of equations). In this week’s blog, Dimitrios Papadomarkakis (student at the National Technical University of Athens), discusses the subject of closed-form (analytical) sol ...[Read More]
Cratons: building blocks of continents and their economic importance
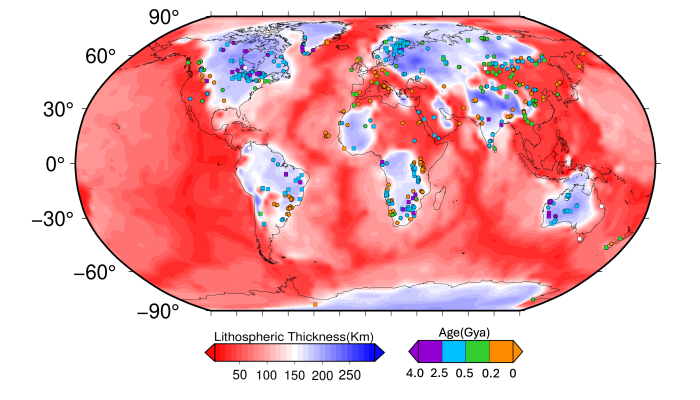
The 4.5 billion years of geologic evolution has shaped the tectonic processes in Earth we see today. Over the span of time, Earth has changed from being a magma ocean to a tectonically active planet, by transitioning through different tectonic regimes. A silent witness of this journey have been cratons which have survived for billions of years. Therefore cratons preserve clues of past tectonic pr ...[Read More]
Growing geological Christmas trees: salt ‘Christmas-tree’ structures explained
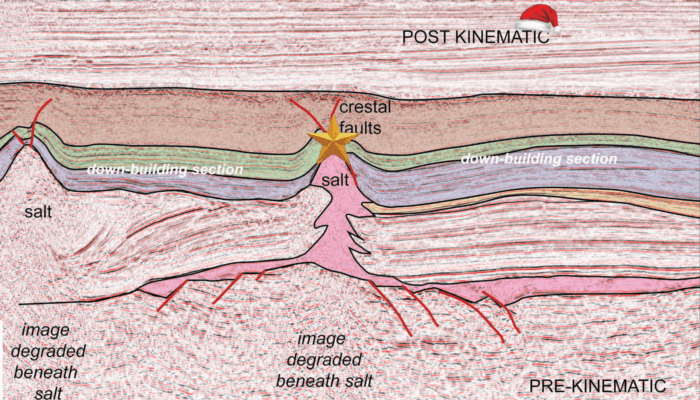
As geoscientists, we tend to see geology everywhere. Around Christmas, many people stare at decorated fir trees and twinkling lights; salt tectonicists stare at seismic lines and outcrops and see… trees as well. Tall stems, branching limbs, stacked “tiers” of material; a whole forest of geological Christmas trees hiding in the subsurface. In salt provinces around the world, from the Flinders Range ...[Read More]