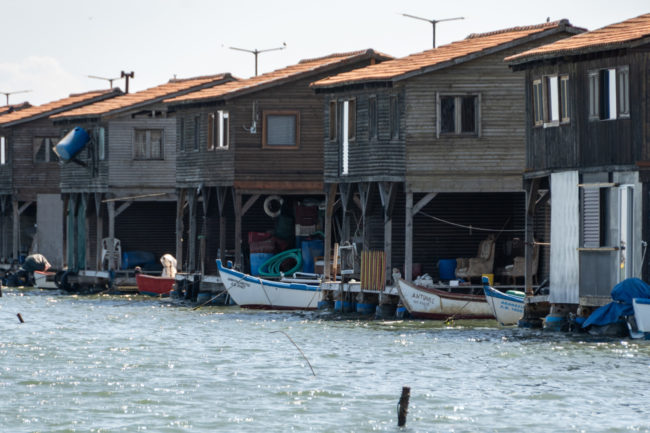
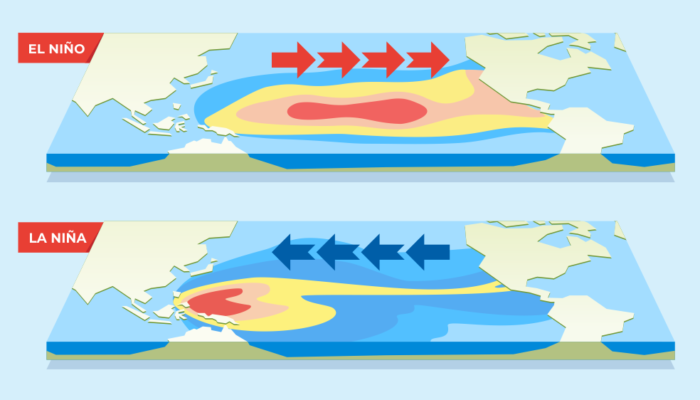
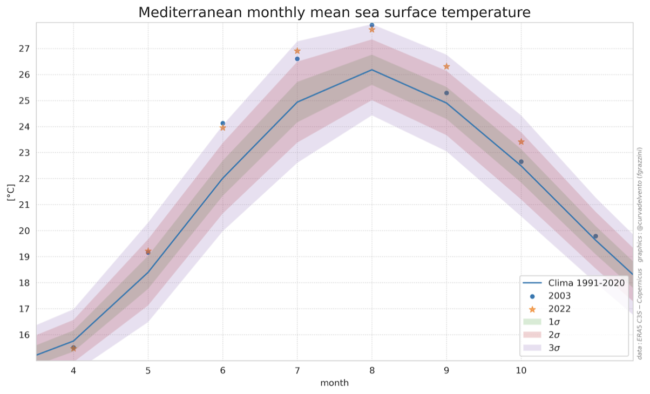
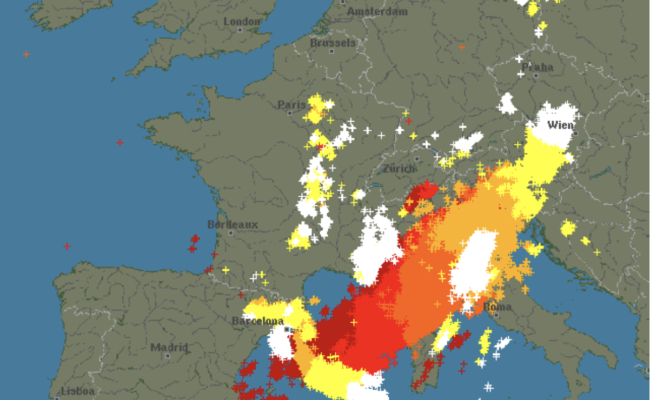
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has just announced that the La Niña episode has officially ended, and from autumn onwards, it should give way to an El Niño phase. But what does that mean? And what is the influence of these weather phenomena on global warming?For those who have never heard of La Niña before, here’s an explanation of this phenomenon. The Earth rotates, so there are ...[Read More]
El Niño is back: What it Means for Global Warming?