The GeoMOD meeting is a bi-annual conference that gathers Earth Science researchers from all over the world working on analogue and numerical modelling in Geosciences. Showcasing the most recent advances in this field, GeoMOD brings together the pursuit of new knowledge while allowing for great get-togethers between researchers. This year’s meeting was successfully held in Lisbon but not without i ...[Read More]
Simulating the Deep Earth with MAGEMin: A Toolkit for Thermodynamic Modeling in Geodynamics
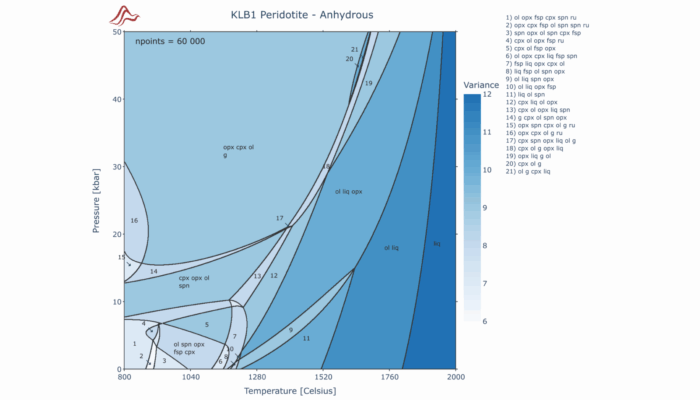
Understanding how rocks melt, deform, and evolve within Earth’s interior is a central challenge in geoscience. These processes span a wide range of spatial and temporal scales and are governed by complex interactions between temperature, pressure, composition, and phase stability. Capturing this complexity in numerical models requires integrating mineral thermodynamics directly into geodynamic mod ...[Read More]
How numerical modeling helps decipher the dynamics and evolution of Venus
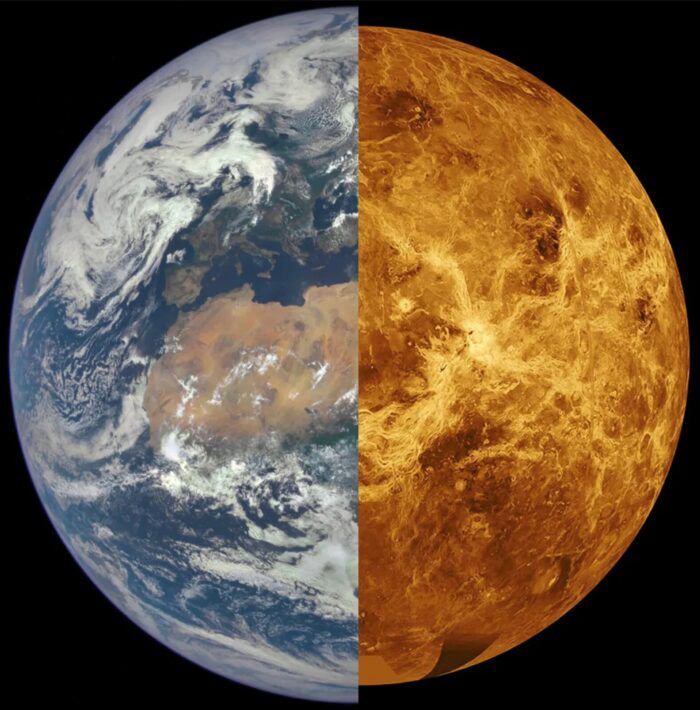
Earth’s sister, Venus, is a planet whose evolution is drastically different from our own. Unravelling the hidden mysteries behind the divergent evolution of these two planets could hold the key to understanding what makes a planet habitable. Using numerical modelling, Diogo Lourenço and Cédric Gillmann unveil the dynamics of Venus while linking them to observations. In today’s blog pos ...[Read More]
Coexisting Forces in Geodynamic Modelling: Pros, Cons, and Synergies of Analogue and Numerical Modelling
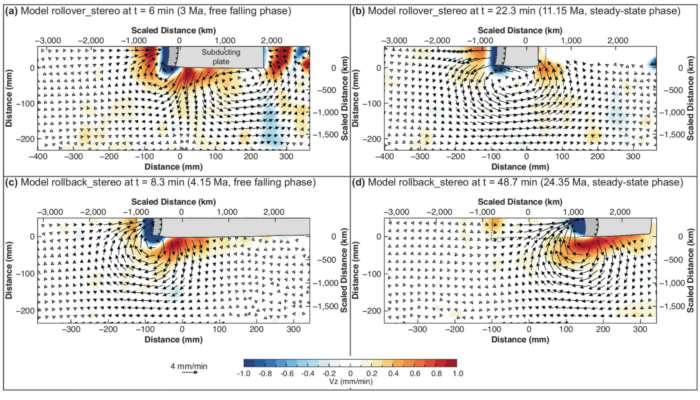
Geodynamic modelling helps us understand Earth’s internal processes by providing a framework to test hypotheses. Analogue modelling uses physical models governed by the laws of nature, with resolution down to Planck’s length. In contrast, numerical modelling employs mathematical methods to approximate solutions to the physical laws governing Earth’s processes. Each modelling approach comes with it ...[Read More]