The NPG paper of the month for February 2023 was awarded to “A Range of Outcomes: The Combined Effects of Internal Variability and Anthropogenic Forcing on Regional Climate Trends over Europe” by Clara Deser and Adam S. Phillips. How much will Europe warm in the next 50 years? Will precipitation increase or decrease? Are past climate trends unique or could alternate realities have exis ...[Read More]
Socio-economic and security implications of global heating
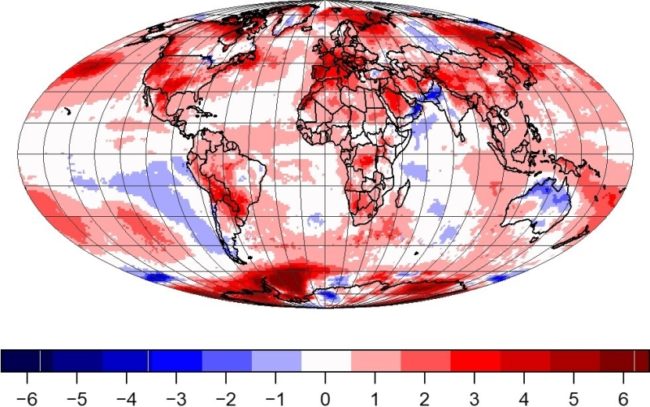
This year, like in the last few years, we are experiencing the effects of global heating in increasingly personal ways. The summer of 2022 exposed us to ever more extreme heat waves in North America, Europe, and Asia. For instance, the heat wave in India and Pakistan reached temperatures of 49C in Nawabshah, Pakistan. North America too experienced devastating heat waves and wildfires. Los Angeles ...[Read More]
ECS SpotLight: Changes in the climate dynamics have already modified characteristics and impacts of storms in France: the case study of storm Alex 2020
Extratropical cyclones play a key role in modulating the precipitation and wind in mid-latitudes and can be responsible for extreme wet and windy events. With global warming, the dynamics and thermodynamics associated with these atmospheric systems are being affected. However, due to the complexity of modelling the climate system, a challenge arises when evaluating the influence that climate chang ...[Read More]
Back in Green: The Return of Pineapple Express to California
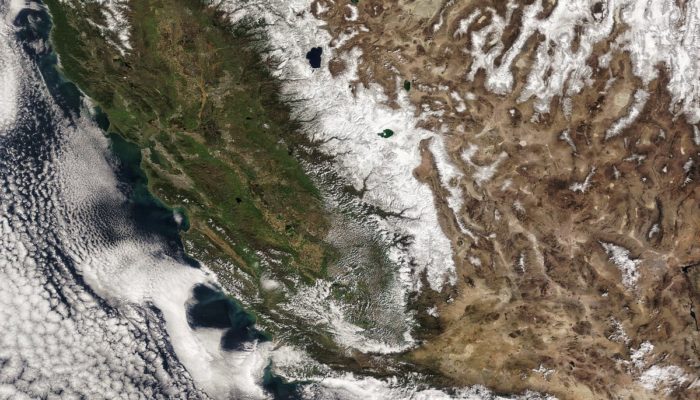

If you Google Pineapple Express you’re likely to end-up with a stoner movie comedy, but for those who live on the West Coast of North America, it has an entirely different meaning. Pineapple Express is a weather phenomenon that refers to a strong atmospheric river that brings heavy rain and moisture to the region. Despite the shared name, the two Pineapple Expresses couldn’t be more di ...[Read More]

