Keeping up with current Machine Learning (ML) developments in hydrology can seem like a never-ending game of catch-up! Instead of drowning yourself in a heap of scientific publications, here are a few practical hints to help you stay ahead in the ever-evolving intersection of ML and hydrology. Hint 1: Surround Yourself with Experts and Like-Minded ML Enthusiasts When questioned about how they keep ...[Read More]
When Droughts Dry Up Power: The Climate-Hydropower dilemma
When we think of hydropower, its environmental impacts usually comes to mind: the dams that disrupt ecosystems, the water bodies that shift, the surface evaporation that increases, and the greenhouse gases that escape from reservoirs1. Hydropower, for all its clean energy potential, is not without its environmental baggage, whether on local water resources or the global surface water storage. But ...[Read More]
CrowdWater: A Citizen Science Revolution for Flood Prediction with Machine Learning
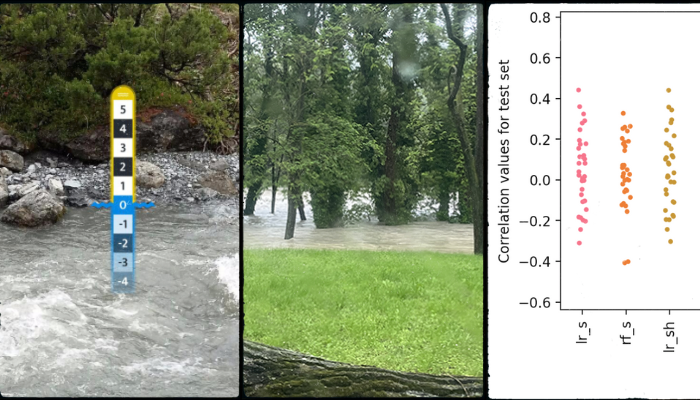
CrowdWater is a citizen science project that enables the collection and sharing of water level data on streams and rivers worldwide using virtual scales. As part of the project, a CrowdWater (CW) mobile application was developed that allows users to take and upload geo-referenced photos of water bodies, which are then processed and stored in a global database. CW data provides valuable information ...[Read More]
Behind every robust result is a robust method: Perspectives from a hydrological case study
Scientific studies and mathematical models are increasingly used to guide the management and development of society. But while science and modelling can indeed provide a robust basis for decision making, we must be mindful of two related considerations. First, science is based not on trust but on skepticism, meticulous technique and careful verification. Second, science is not made of absolute tru ...[Read More]