Recently, the European Geosciences Union (EGU) started to support a new type of event called ‘Campfires’ that will give the Divisions the freedom to run online interactive events in a way that suits their needs. This allows the EGU Divisions to encourage interactions in their research communities through virtual informal meetings. In this framework, and thanks to a group of young and established s ...[Read More]
NPG Paper of the Month: “Statistical postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for severe weather at Deutscher Wetterdienst”
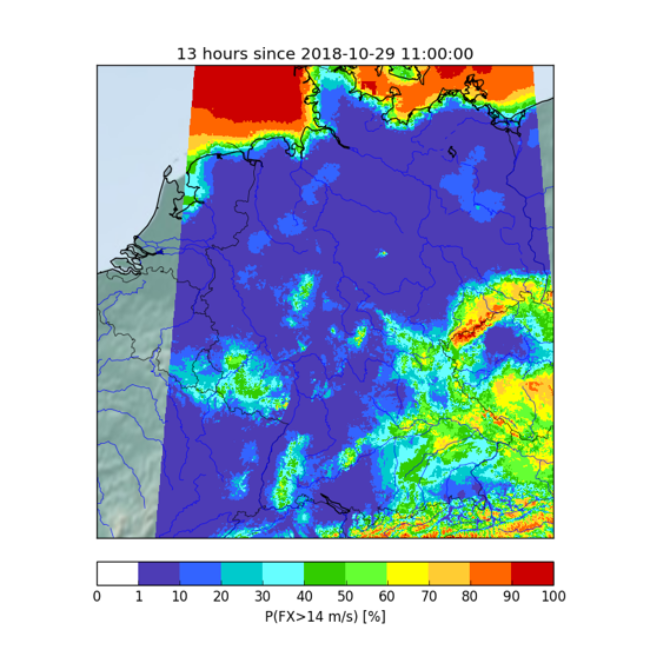
The October 2020 NPG Paper of the Month award goes to Reinhold Hess for the paper “Statistical postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for severe weather at Deutscher Wetterdienst“. Ensemble Forecasting rose with the understanding of the limited predictability of weather. In a perfect ensemble system, the obtained ensemble of forecasts expresses the distribution of possible weather scena ...[Read More]
The never-ending 2020 hurricane season
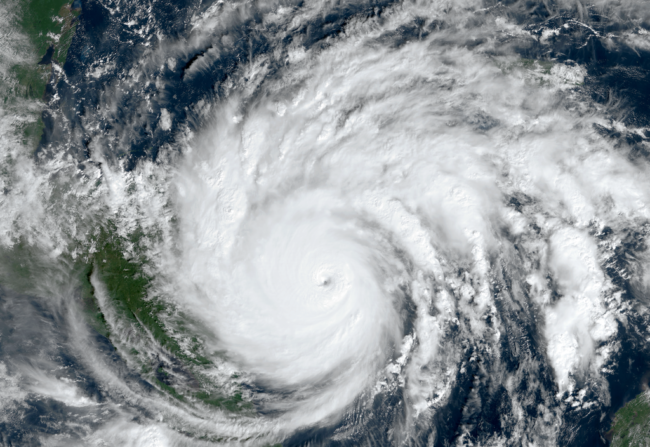

Iota, this is the name of the last category 5 hurricane in the Atlantic Ocean. Iota is a non-name because normally hurricanes are named by NOAA starting from A to Z but when the alphabet is over, they are just identified from a letter of the Greek alphabet. Iota is a special cyclone not just because its name implies that the hurricane season is particularly rich in storms but also because of its e ...[Read More]
Can we connect the exceptional floods in France and Italy associated with the storm Alex to climate change?
The first days of October were marked by an extreme weather event: storm Alex, a cyclone of Atlantic origin, caused massive showers and thunderstorms over Provence, the Alps, Piedmont and Liguria. In these regions, numerous historical records of precipitation were broken causing the flooding of several streams and rivers in which many people lost their lives. Economic damage was also significant a ...[Read More]

