Hydrological change is one of the clearest signals of climate variability and human impact on the environment. Yet detecting these changes reliably requires robust, long-term data from river basins that are as close to “natural” as possible, with little influence from dams, abstractions, land use change or any other human influences. That’s where the ROBIN project comes in. ROBIN, or the Referenc ...[Read More]
ROBIN: Tracking Climate Change Through the World’s Most Natural Rivers
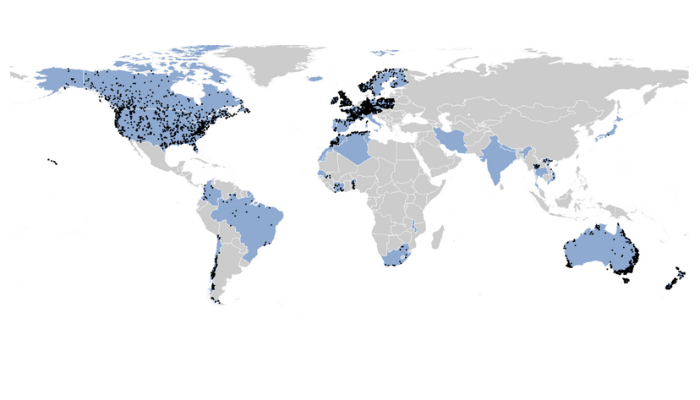
Distribution of countries participating in the first Phase of the ROBIN Network (blue shading). Black dots are stations included in the first iteration of the ROBIN dataset. Reproduced from Turner et. al. (2025)
