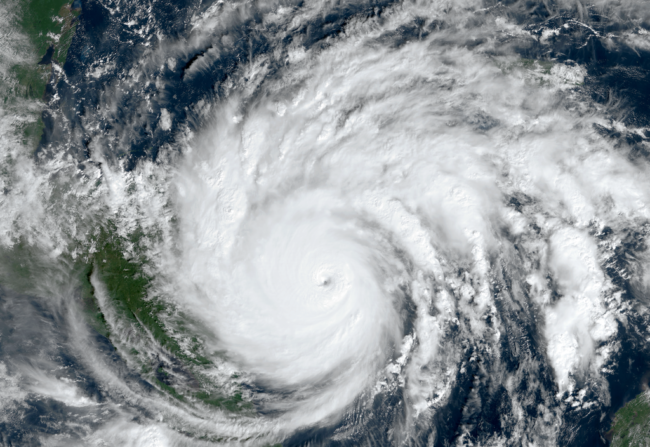
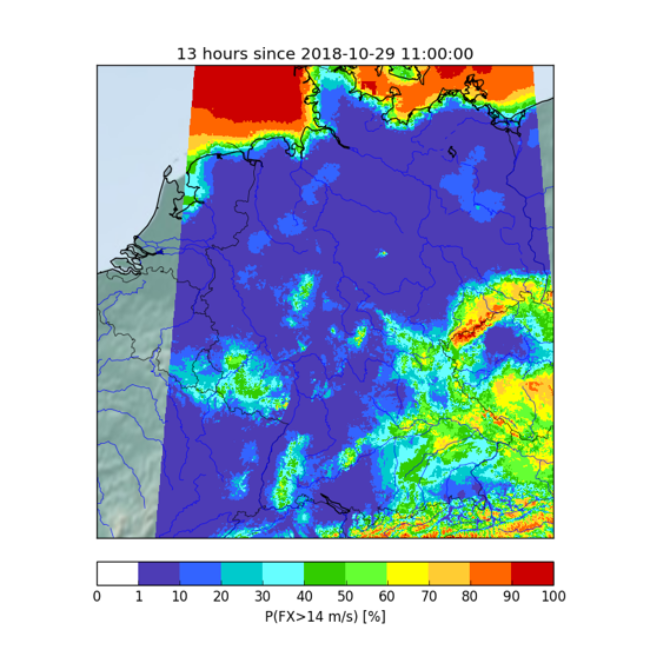
The October 2020 NPG Paper of the Month award goes to Reinhold Hess for the paper “Statistical postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for severe weather at Deutscher Wetterdienst“. Ensemble Forecasting rose with the understanding of the limited predictability of weather. In a perfect ensemble system, the obtained ensemble of forecasts expresses the distribution of possible weather scena ...[Read More]
NPG Paper of the Month: “Statistical postprocessing of ensemble forecasts for severe weather at Deutscher Wetterdienst”