One year ago, Vincenzo Carbone left us. Vincenzo was a leading scientist in nonlinear geophysics, turbulence, and complex systems, influencing fluid and plasma physics, weather and space weather, solar–terrestrial relations, and climate dynamics. Yet for those who worked closely with him, his legacy goes well beyond his remarkable scientific achievements. Scientific Contributions and Impact Over m ...[Read More]
Rethinking the carbon cost of scientific exchange: Nonlinear effects of reducing scientific mobility
The carbon footprint of scientific collaboration has become an increasingly debated topic. Conferences, workshops, and research travel remain central to how science function, yet they also contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions. Since the pandemic era scientists also learned to work virtually and to attend workshops and conferences online. Understanding the carbon footprint, and how it comp ...[Read More]
AI-generated Images: the fragility of visual evidence in geosciences
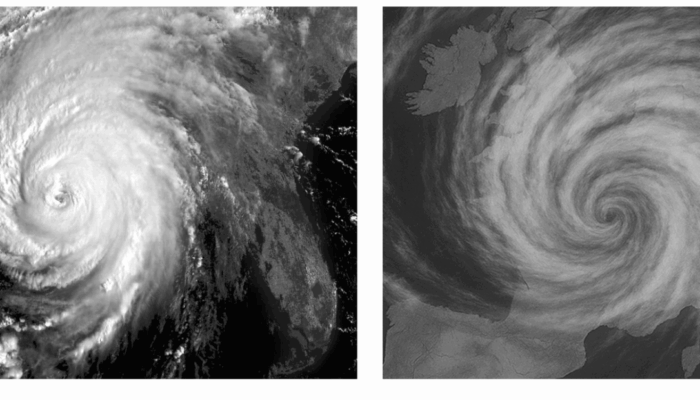
Recently, an increased number of visually striking “scientific” images have been found online: snapshots of turbulent flows with dreamlike structure, eerily symmetric cloud patterns, and what appeared to be global temperature fields annotated with plausible colormaps and scientific-looking labels. Many of these posts quickly go viral on social media. And yet, in many cases, the images ...[Read More]
Sea level rise: a global threat in a warming planet
Over 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by seas and oceans but in the geological past the extension of sea and land has varied several times as sea level changed over time. During the past millions of years, the oceans have cyclically retreated and expanded with the alternating of warmer and colder climatic periods in consequence of the astronomical motions of the Earth, repeatedly changi ...[Read More]