An emerging problem brought by climate change is the on-going deoxygenation of the world’s oceans. The fact that concentrations of dissolved oxygen have been/are declining in both open-ocean and coastal waters is becoming a major scientific and societal concern raised in the Kiel Declaration and in the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) 2019 report. Lower levels of dissolved oxy ...[Read More]
The most-read NPG 2020 paper: “Effects of upwelling duration and phytoplankton growth regime on dissolved-oxygen levels in an idealized Iberian Peninsula upwelling system”
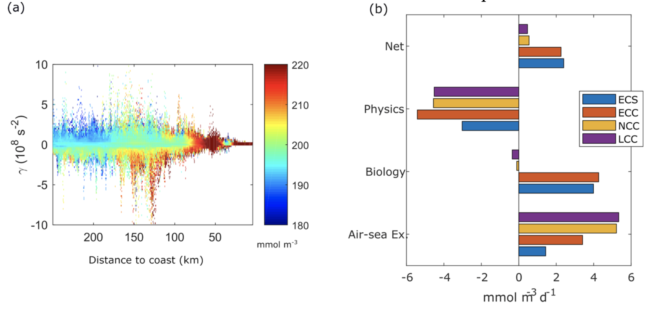
(a) Snapshot of dissolved oxygen distribution in the upwelling front instabilities for the ECS simulation (γ is the Okubo-Weiss criterion). (b) Dissolved Oxygen budget in the idealized Iberian Peninsula Upwelling System. Net value is the sum of Physical, Biological and Atmospheric processes that change oxygen concentration levels. Physics accounts for the effect of upwelled subsurface waters and offshore transport by upwelling front instabilities. Biology term accounts for oxygen photosynthetic production and community respiration. Simulations performed are ECS (short upwelling season with enhanced phytoplankton growth), ECC (long upwelling season with enhanced phytoplankton growth), NCC (long upwelling season with neutral phytoplankton growth) and LCC (long upwelling season with limited phytoplankton growth).
License: Effects of upwelling duration and phytoplankton growth regime on dissolved-oxygen levels in an idealized Iberian Peninsula upwelling system.

