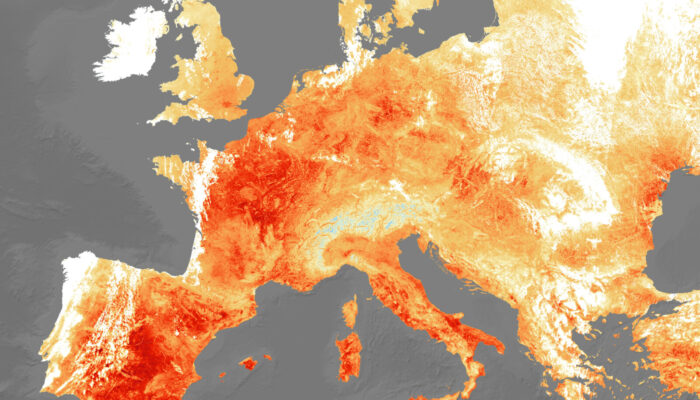
Persistent atmospheric circulation patterns are not a necessary requirement for warm temperature extremes in Europe. This key finding from a recent study led by Emma Holmberg challenges a more traditional meteorological view of persistence, which typically considers summertime heatwaves, especially in northern regions of Europe, to be synonymous with persistent atmospheric flow patterns. Furthermo ...[Read More]
NPG Paper of the Month: “A Range of Outcomes: The Combined Effects of Internal Variability and Anthropogenic Forcing on Regional Climate Trends over Europe”
The NPG paper of the month for February 2023 was awarded to “A Range of Outcomes: The Combined Effects of Internal Variability and Anthropogenic Forcing on Regional Climate Trends over Europe” by Clara Deser and Adam S. Phillips. How much will Europe warm in the next 50 years? Will precipitation increase or decrease? Are past climate trends unique or could alternate realities have exis ...[Read More]
Socio-economic and security implications of global heating
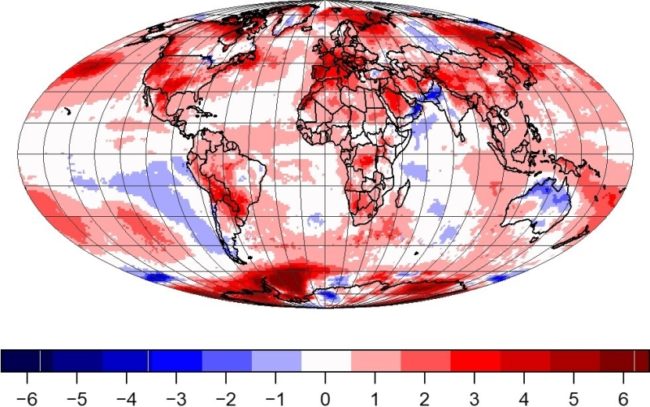
This year, like in the last few years, we are experiencing the effects of global heating in increasingly personal ways. The summer of 2022 exposed us to ever more extreme heat waves in North America, Europe, and Asia. For instance, the heat wave in India and Pakistan reached temperatures of 49C in Nawabshah, Pakistan. North America too experienced devastating heat waves and wildfires. Los Angeles ...[Read More]
ECS SpotLight: Climate change on extreme winds already affects off-shore wind energy availability in Europe
Off-shore wind energy plays a key role in the transition to a renewable energy (RE) system, and its usage is expected to increase in the next few decades. Nevertheless, wind energy is one of the most variable and weather-dependent RE, because of its natural dependence on the wind speed, which can vary at different time scales, ranging from small-scale turbulence to seasonal oscillations and up to ...[Read More]