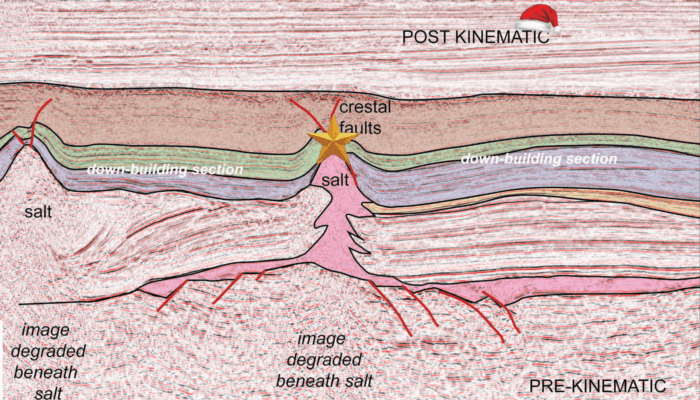
As geoscientists, we tend to see geology everywhere. Around Christmas, many people stare at decorated fir trees and twinkling lights; salt tectonicists stare at seismic lines and outcrops and see… trees as well. Tall stems, branching limbs, stacked “tiers” of material; a whole forest of geological Christmas trees hiding in the subsurface. In salt provinces around the world, from the Flinders Range ...[Read More]
Growing geological Christmas trees: salt ‘Christmas-tree’ structures explained