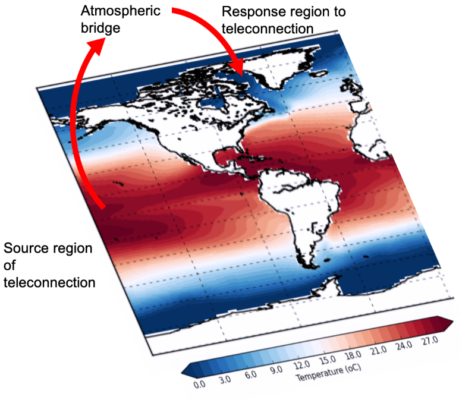
We know that climate change is being felt worldwide, but it is especially prominent in the Arctic, where temperatures are warming twice as fast as anywhere else on the planet. This especially sensitive environment, whose icy, snow-covered land and sea is so important in the global climate system, is really starting to feel the heat. But where is this heat coming from? In this blog post, we will ex ...[Read More]
Climate Change & Cryosphere – The tropical fingerprint in Arctic climate