As a New Englander interested in weather, I was used to a fairly intuitive air temperature split between rain and snow. Once air temperature got slightly above freezing, I’d commonly see rainfall with snowfall more frequent below freezing. Then something happened when I moved to the Intermountain West of the United States. Instead of seeing rain when it was slightly above freezing, I’d see snow at ...[Read More]
Did you know there’s a place to Find, Discover, & Download Arctic Data? Meet The Arctic Data Center!
Getting data from the Arctic is often difficult and expensive – instead, stand on the shoulders of giants and investigate over 6000 datasets preserved for future download and reuse in the Arctic Data Center! Read on for more information about the Arctic Data Center and the data contained therein. The Arctic Data Center is the primary data repository for the Arctic section of the US National ...[Read More]
Did you know … that liquid water can be held within a glacier?
Hidden below the surface of some glaciers, liquid water can be found within what is called the firn layer – the upper layer of a glacier where snow compacts into glacier ice. Liquid water may persist there for up to many years, forming what scientists call “firn aquifers.” While observations of seasonal firn aquifers have existed since the mid to late 1900s in several mountain glaciers, recent stu ...[Read More]
Atmospheric Rivers: A blanket for Antarctic winter sea ice
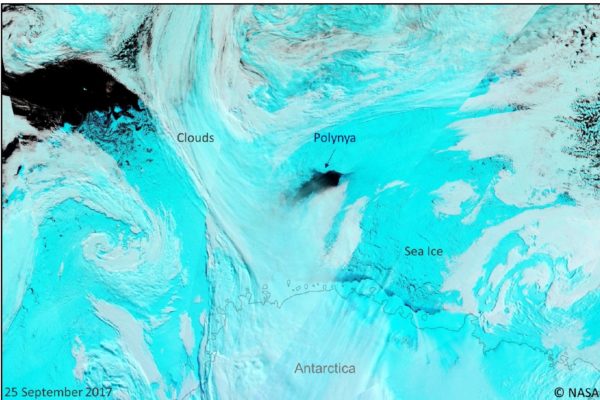
The mysterious appearance and disappearance of the Weddell Polynya, a giant hole in the sea ice cover, has long puzzled scientists. Recent work reveals that the polynya is initiated and maintained by gigantic and formidable atmospheric currents: atmospheric rivers! Read on to find out more… Each year, approximately 15 million square kilometers of ice forms in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica d ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Icebergs increase heat flux to glacier
Icebergs are ubiquitous in Greenland’s fjords, melting and releasing freshwater as they float towards the open ocean. The amount of freshwater released from these icebergs can be vast – the equivalent of around 50,000 Olympic swimming pools per day in some fjords. New research reveals that this freshwater causes fjord currents to speed-up, which can actually increase the amount of heat delivered t ...[Read More]
Cryo-massy Films

There are countless Christmas films, and almost all of them feature some form of snow, ice or cold weather. There are the classics such as Home Alone, Elf and Miracle on 34th Street, and there are the newer, shall we say ‘Netflix’ style, which feature Princes, Knights and Vanessa Hudgens. There’s just no way to watch them all over the festive period, so let us recommend you our top 5 Christmas fil ...[Read More]
Time To Reflect
Albedo or albedon’t? One possible solution to global warming is to turn everything white to increase the planet’s albedo, i.e. how reflective it is (see, for example, this website). A higher albedo would be one way to reduce global warming, by reducing the amount of incoming shortwave solar radiation absorbed by the planet’s surface, which is then re-emitted as longwave radiation that ...[Read More]
Hysteresis For Dummies – Why history matters
Perhaps you have stumbled upon the word ‘hysteresis’ before, for example in connection with the stability behavior of our Earth’s large ice sheets and their long-term effect on global sea-level rise, or the long-term stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or even in another context outside earth/climate science. Or you might have come across this term during your studies, bu ...[Read More]
Seafloor secrets: traces of the past Patagonian ice sheet
Today’s Patagonian ice caps are confined to the high-altitude Andean Mountain range as the Northern and Southern Patagonia ice fields, and they are rapidly melting. The southern part of the Patagonian ice cap drains partially through fast-flowing ice streams into the fjords of Patagonia. Glaciers in this region have been losing ice at accelerating rates by large calving events, due to rising globa ...[Read More]
Did you know… that you can read the edge of Greenland’s ice as an open book?
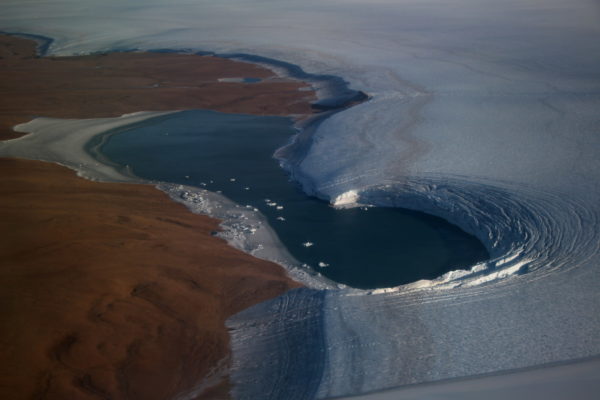

Scientists struggle to get ice samples from the depths of glaciers where fundamental pieces of information about the climate of Earth are stored. But in many places around the periphery of the Greenland Ice Sheet, you don’t need to drill a deep ice core to obtain ancient ice, you can simply walk across the ice sheet’s margin and look at the layered ice surface. There you can read the ice as though ...[Read More]


