In this Must Read paper “3D seismic analysis of the structure and evolution of a salt-influenced normal fault zone: a test of competing fault growth models (2013)”, by Christopher A-L. Jackson and Atle Rotevatn used detailed 3D seismic reflection data from the Suez Rift, Egypt, to gain a better understanding of the structural evolution of normal faults. Specifically, the paper shows th ...[Read More]
Geology Bites: Podcast conversations about geology with researchers making key contributions to our understanding of the Earth and the Solar System
As readers of this blog know, geology is an awe-inspiring subject, dealing as it does with immensely powerful forces operating on time scales, pressures, and temperatures we can barely fathom. It is geological processes that are responsible for the continents, oceans, mountain ranges, indeed for all the landscapes we see around us. Even though many of these processes operate over deep time and dee ...[Read More]
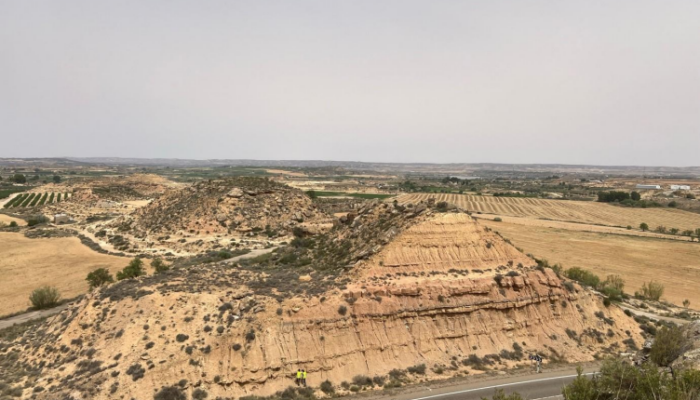
Inverted River Channels in Alcaniz: Insights into Mars’ Fluvial History
This edition of ‘Features from the field’ is brought to you by Faris Beg, a masters student on the EU Erasmus Mundus Joint Master’s program in planetary geosciences—GeoPlaNet. This blog is a result of a geological field excursion carried out collectively in groups by students, organized by the GeoPlaNet consortium in Alcañiz, Spain. He will be talking about his observations and l ...[Read More]
TS Must-Read – Peron-Pinvidic et al. (2013) Structural comparison of archetypal Atlantic rifted margins: A review of observations and concepts
Rifted margins are regions at the transition from oceanic to continental crust, formed by the stretching and thinning of the Earth’s lithosphere before the creation of new ocean basins. The study focused on three key transects across Atlantic rifted margins. In their 2013 article in Marine and Petroleum Geology, Peron-Pinvidic et al. present a comparative analysis of the architecture of vari ...[Read More]
TS Must-Read – Wang et al. (2012) Deformation cycles of subduction earthquakes in a viscoelastic Earth
Large subduction earthquakes cause perturbation of the subduction system, whose response depends on its rheological characteristics. The evolution of the subduction system from earthquake to earthquake is defined as subduction earthquake cycle (SEC), and is characterised by three main processes that operate over decades/centuries: postseismic afterslip, viscoelastic mantle relaxation, and fault re ...[Read More]
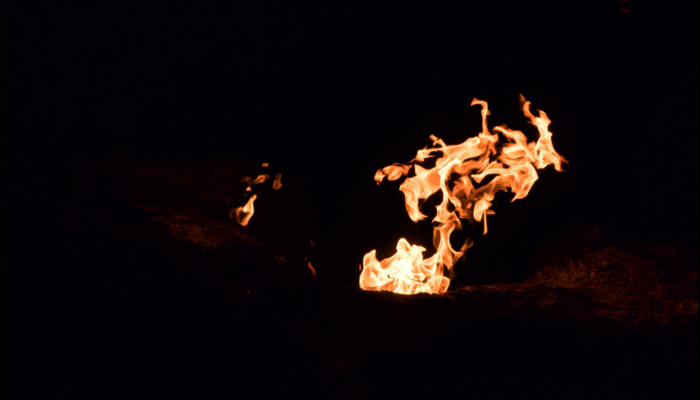
Geomythology. Chimera: the lion, the goat, the snake and the flaming gas vents
Once upon a time in Lycia there was a land of fire, which burned so bright the light was visible by sailors navigating on the Mare Lycium, who were using the fires as a natural lighthouse. Mount Chimaera in the country of Phaselis is on fire, and indeed burns with a flame that does not die by day or night Those were the words of Pliny the Elder in his Naturalis Historia (2.110). Ancient Lycia is n ...[Read More]
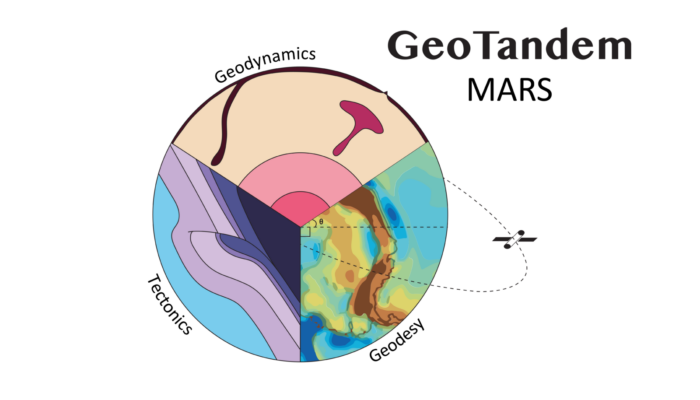
Geotandem: The Tectonics (or lack thereof) of Mars
Welcome to the first of its kind, the Geotandem 01! A collaborative series between EGU divisions. Interdisciplinarity is intrinsic to Geosciences, so we want to showcase how researchers approach the same topics from different but also complementing perspectives. In each edition, we will bring you a high-interest topic for the community seen from the eyes of diverse disciplines. Today, the Tectonic ...[Read More]
TS Must-Read – Mancktelow (2008): Tectonic pressure: Theoretical concepts and modelled examples
Neil Mancktelow published this Must-Read paper on the concept of “tectonic pressure” in 2008. The paper reviews previous work and theoretical concepts published on this fundamental topic. Additionally, numerical models that estimate the magnitude of tectonic pressure variations are presented for several realistic natural structures, such as folds, boudins, and inclusions. The premise of tectonic p ...[Read More]
TS Must-Read – Bürgmann and Dresen (2008): Rheology of the Lower Crust and Upper Mantle: Evidence from Rock Mechanics, Geodesy and Field Observations
In 2008 Roland Bürgmann and Georg Dresen published their Must-Read paper on the rheology of the lower crust and upper mantle, based on findings from the lab, the field and space. As stated in the introduction, “rheology is the study of the flow and deformation of all forms of matter,” and as such the rheology of the Earth’s lower crust and upper mantle is closely linked to the evolution and deform ...[Read More]
TS Must-Read – Hudec and Jackson (2007) Terra infirma: Understanding salt tectonics
The TS Must-Read paper by Hudec and Jackson (2007) provides a combination of analogue models and natural cases to describe, in a review paper, salt flow mechanisms, diapir growth, and the ways these processes interact with regional deformation, in compression and extensional tectonics. Salt is mechanically weak and can flow like a fluid under gravitation, displacement, and thermal lo ...[Read More]