The current retreat of Arctic sea ice is a major sign of ongoing climate changes. And it could almost disappear during summer in a few decades from now, depending on the amount of greenhouse gases we will emit into the atmosphere. In this context, understanding what are the exact causes of this sea-ice loss is important. One of these causes is the amount of heat transported by the ocean (which dep ...[Read More]
It’s not you, it’s me(lange): ice shelf break-up triggered by mélange and sea-ice loss

Between March and May 2007, a total of ~2,445 km2 (equivalent to over 17 football pitches) of ice mélange (a mixture of sea-ice types, icebergs and snow) and part of Voyeykov Ice Shelf in East Antarctica rapidly broke up. Observations of the timing and triggers of such events are relatively rare in East Antarctica, compared to ice shelves on the Antarctic Peninsula. Recent work highlights the impo ...[Read More]
Women of Cryo III: Women monitoring the Peruvian glaciers
The ruins of a hidden majestic city as Machupicchu in Peru immediately call for our attention. However, there are far more beautiful attractions found hidden amongst the landscape, such as the glaciers, high mountains or the cultural heritage in the area. In South America, glacial bodies are geographically restricted to the Andes, the mountain range that runs across the continent from the tropics ...[Read More]
The “Cliffs Notes” on Ice-Cliff Failure

The retreat of large glaciers that drain the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets could expose immense ice-cliffs at newly-bared calving faces, which are the exposed ends of glaciers where, in these cases, glacier ice meets the ocean. Past a certain height, these ice cliffs will become susceptible to collapsing from high stresses, a process known as structural ice-cliff failure. If a taller ice clif ...[Read More]
Introducing TJ Young, our new early-career representative for the cryo-division of the EGU!
Every two years, the Cryospheric Sciences division of the European Geophysical Union (EGU) elects a new representative for its early-career scientists. Starting in April 2021, Tun Jan (TJ) Young will take over the role from Jenny Turton, who is the outgoing representative. TJ shares a bit about himself and how his previous leadership experience aligns with the goals of EGU’s early career scientist ...[Read More]
Cryo tips to make the most of vEGU21
Similar to last year, this year’s annual general assembly is fully virtual. But unlike last year, the in-person experience is back! There are short courses, networking events and a website which looks just like the real Vienna Conference Centre. So go and buy yourself a Viennese Sachertorte, brew a batch of coffee and take 5 minutes to look at our top recommendations for vEGU21. vEGU21 – wha ...[Read More]
On snowmelt, water security, and a warming climate – Why solution-oriented research matters, now more than ever
1 April 2015: for the first time on record, the chief of the California Cooperative Snow Surveys, Frank Gehrke, had no snow to measure at the Phillips Snow Course near Lake Tahoe at the end of the winter. This was in some ways unsurprising, as California had been in a drought since 2012. But drought was nothing new in the state, and this was the first time on record that snow was completely absent ...[Read More]
The new glacial geomorphological map from New Zealand
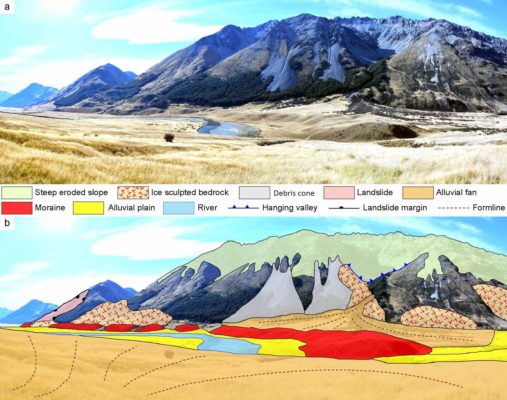
Geomorphological maps are a fundamental tool to represent landforms and understand how different morphological elements and agents shaped a natural landscape. They are also important as background information for many fields of research including ecology, forestry and of course, glaciology. In this week’s blog, Levan Tielidze tells us about the importance of mapping glacial geomorphology, presenti ...[Read More]
Do meditation and a better science correlate? – Mindfulness in Academia
We often start searching for the term “mental health” online only when mental issues are already arising. It seems to be a trendy word on everyone’s social media. Of course, you don’t have to suffer already in order to learn about, and benefit from, mindfulness – or the ability to notice the present moment and what is going on in your life. In this post, I am sharing how I became a more mindful sc ...[Read More]
Climate Change and Cryosphere – What can we learn from the smallest, most vulnerable glaciers in the Ötztal Alps?
The Alps were the first mountains to be studied from a glaciological point of view in the 19th century and they host some of the most studied glaciers of Earth. Some of them are found in the Central Alps and in particular, the Ötztal Alps. Just to cite the most known and largest glaciers in this Alpine sector, we can mention Hintereisferner or Vernagtferner. But in the Ötztal Alps you can also fin ...[Read More]

