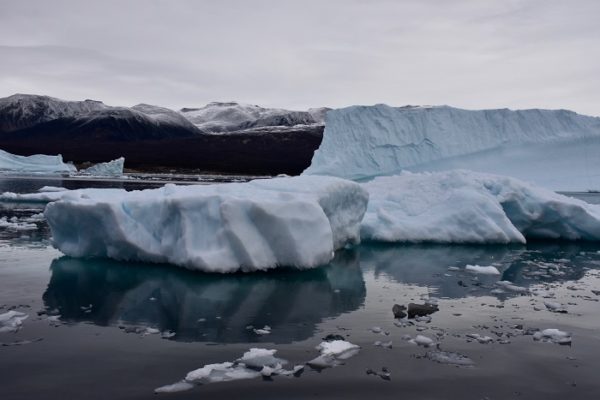
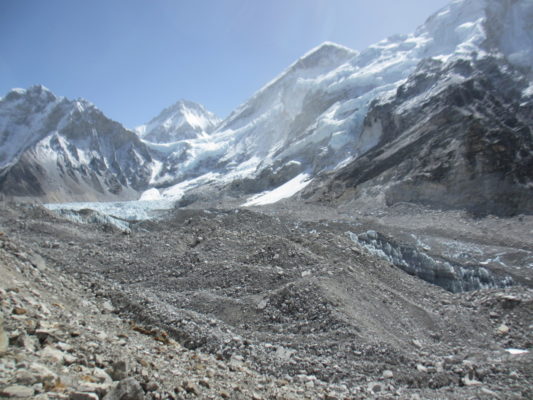
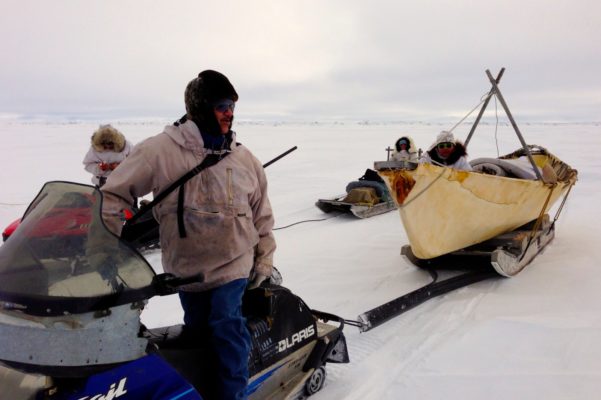
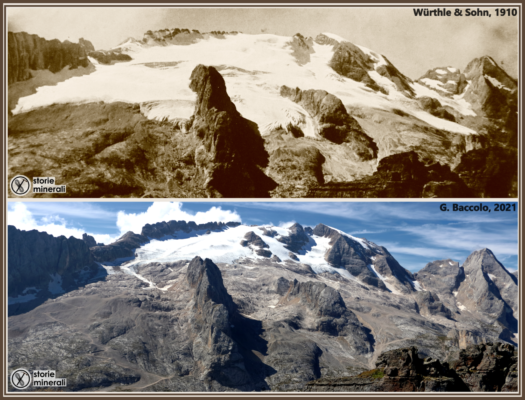
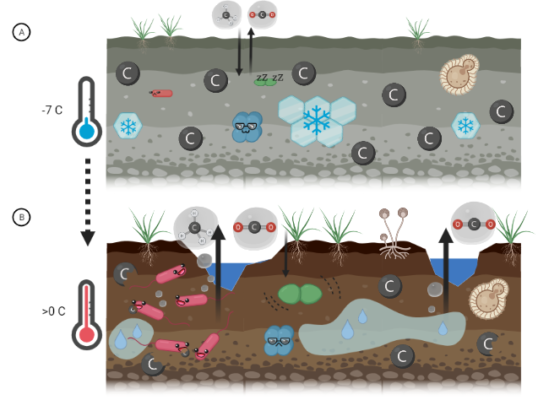
The latest climate models show that Arctic precipitation is changing more rapidly than previously projected with an earlier transition to a rainfall-dominated precipitation. This rapid change in precipitation will have huge implications for the Arctic ecosystem as well as those who live within the region. Arctic precipitation change, why is it so important? The rapid change in Arctic climate, from ...[Read More]
Climate change and cryosphere – A wetter future for the Arctic