On this September 13th, coinciding to be a “Friday 13th”, we wanted to scan the cryo-history for expeditions started, sunken ships that day, and mountain myths. And we did find that. But as autumn approaches in the Northern hemisphere, the spookiest story of all was this one: the unlucky timing of the Arctic sea ice in September. TGIF – but not for sea ice Although the median min ...[Read More]
Dreaming & reading about fieldwork – summer blog break 2024

As we are starting into our annual blog summer break, we reflect on what summer can mean for polar researchers (including some fieldwork saudades). As an Arctic or Alpine cryo-scientist, chances are that you are somewhere in between vacation, fieldwork or trying to work through data while everyone else is free. If you, like us, did not have your vacation yet or do not have any fieldwork com ...[Read More]
SciComm notes: can Granny understand your science?

As an EGU division blog, we facilitate that the most recent cryoscientific insights reach a wider audience. To do this, we have a team of experienced editors (and former authors), but we also love helping first time authors getting experience with outreach. But if you have ever written an outreach piece, you might know that it can be more difficult than expected to write down your research in simp ...[Read More]
You can’t unsee it – the impact of a good visual for scientific data
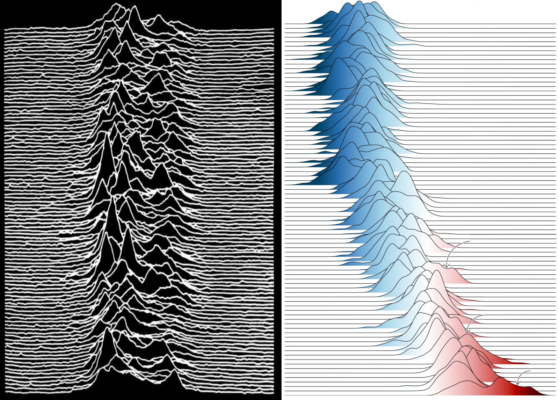
We are visual learners after all and for many of us, creating visual content is far more out of our comfort zone than the already hard earned skills of writing itself. Still, creating an accessible image can be pivotal to not only the success of your paper, but also the reach of your science in general. Today’s post started with a climate figure that went viral because of its similarity to the ico ...[Read More]
Did you know… about worms surviving in permafrost for at least 46000 years?
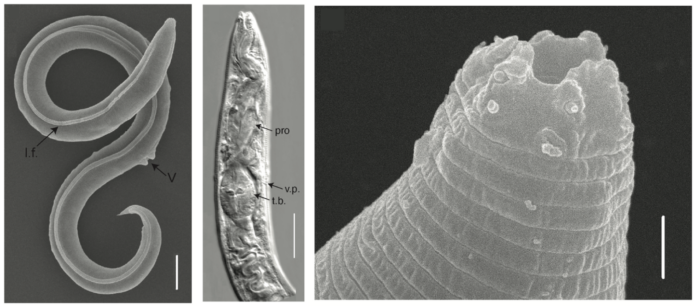
Lately permafrost makes the news more and more because of its enormous carbon stocks and its vulnerability to climate change. While permafrost greenhouse gas budget calculations are complex and harbour an ever-growing research community, its microbial ecology is still on the rise. A recent star are tiny roundworms that survived frozen in permafrost for 46’000 years. Take a short dip into this new ...[Read More]
It’s getting hot in here: Ancient microbes in thawing permafrost
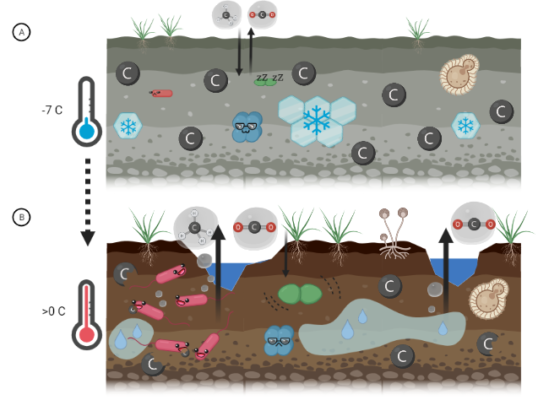
Did you know that the oldest organism on Earth is believed to be a microorganism found in 3-million-year-old permafrost in Siberia? There, it was living at a cosy average temperature of -10 °C at 14 m depth. Or did you hear that some other Arctic soil microorganisms can happily live at extreme temperatures down to -40 °C? Scientists often use these “extreme” microorganisms to get an idea on how ex ...[Read More]

