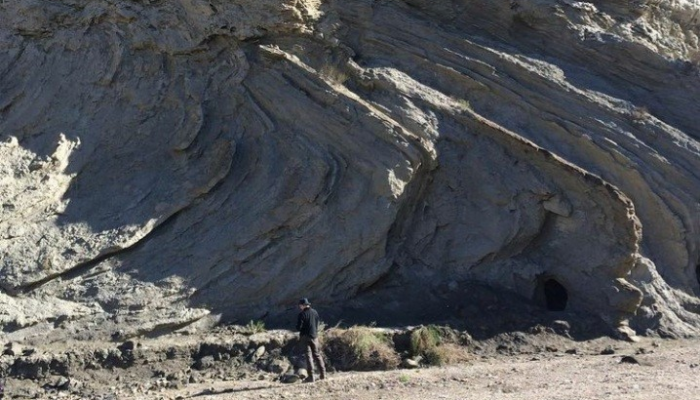
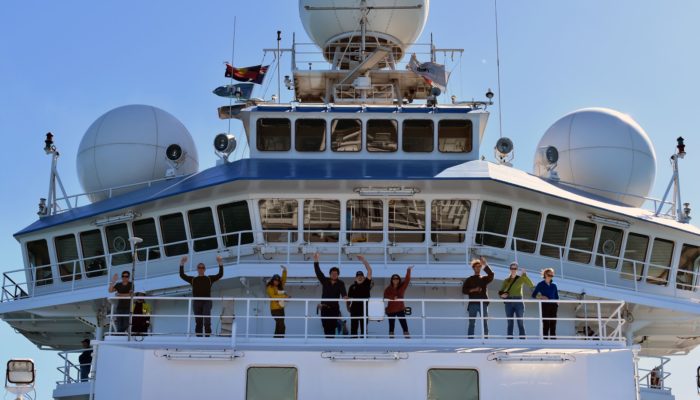
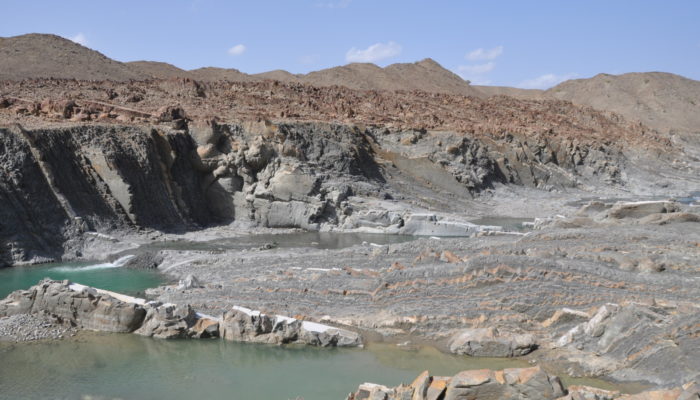
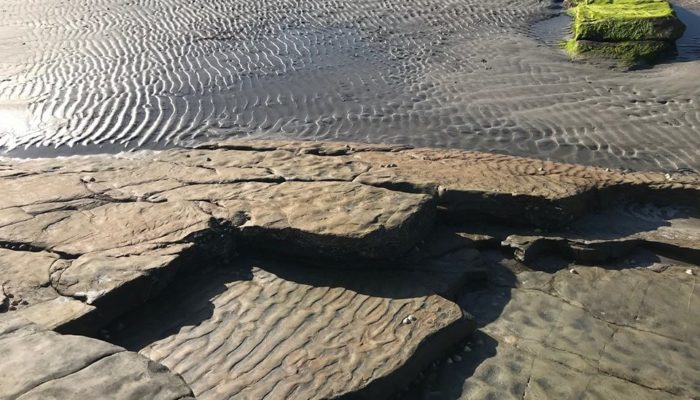
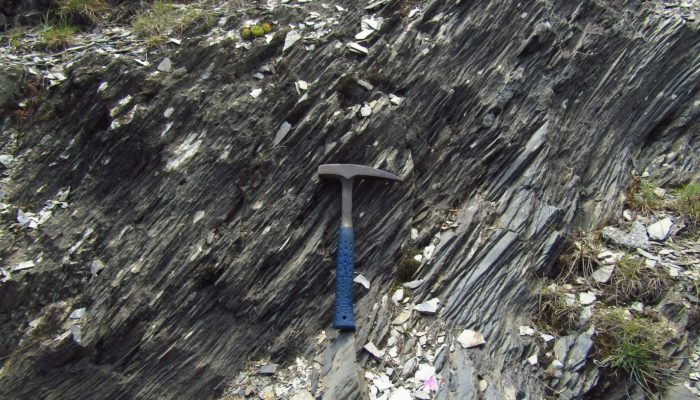
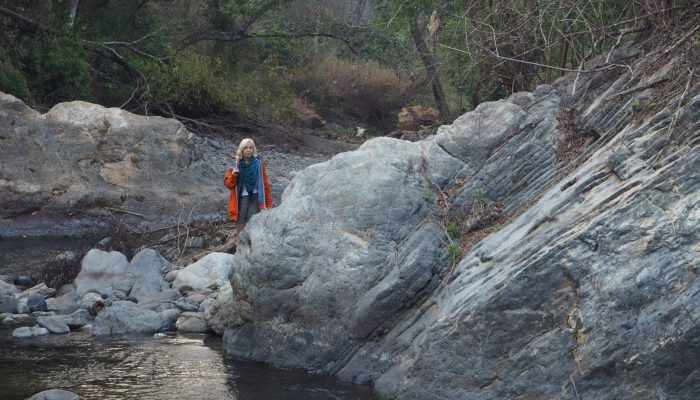
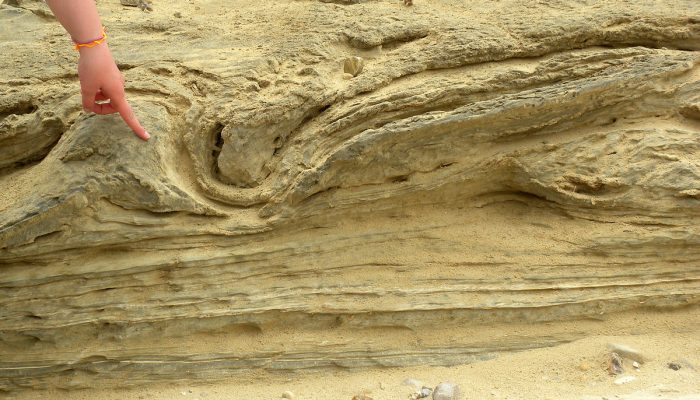
From the time the first Kodak camera in 1888 went on sale we can say with confidence a geologist somewhere was trying to capture field photographs. We love to capture the beauty of the field and every geologist has a story to tell. The EGU would like to connect these stories globally in our new #OnTheRocks series. #OnTheRocks will produce a compilation of geological photographs on different scales ...[Read More]
#OnTheRocks – Because Earth is just beautiful!