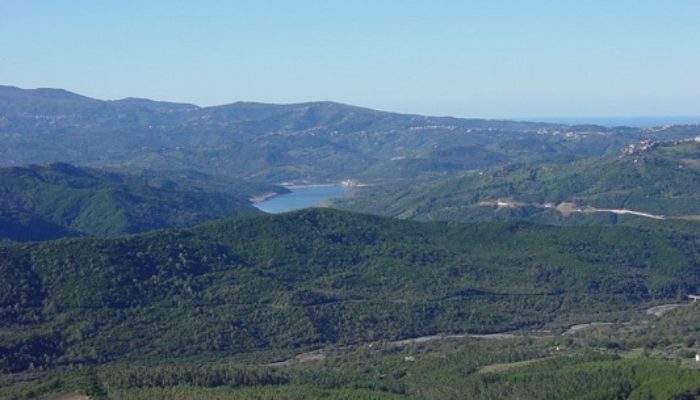
Importance of investigating water fluxes in Mediterranean catchments MOSAIC (Modeling and Observing a mosaic of processes for Soil and water resources management in the Alento critical zone and Implementing adaptation strategies to climate and land use Changes) is an interdisciplinary research program that was established by the Soil Hydrology Group of University of Naples Federico II (Italy) and ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
Across Borders and Sectors
Moving a country for a new job is a big step, but at the same time changing from an industry job to academics is definitely a leap in the unknown. This week Arushi Saxena, currently a post-doc at the University of Florida, writes about her experience taking these two steps at the same time. As geodynamicists, we are well aware that our numerical models are a function of the input parameters. A re ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
TS Must-read – Morgan (1968) Rises, Trenches, Great Faults, and Crustal Blocks
In his 1968 paper “Rises, Trenches, Great Faults, and Crustal Blocks”, Jason Morgan added the missing pieces of the plate tectonics: the representation of plates’ motion in terms of spherical surface, and plate rigidity. In the very first lines of the paper he describes his contribution as an “extension of the transform fault concept [of Wilson, 1965; see the TS-must-read blogpost of October 15, 2 ...[Read More]
Ocean Sciences
Life as a “dry” oceanographer – studying Earth’s oceans from your laptop
I didn’t always know that I would become an oceanographer when I grew up, but I knew I would be doing ‘Science’. I was born and raised in Paris, France. While growing up, I was always interested in Science, from watching documentaries about the universe or nature, to attending science events at museums. While Science is very wide and encompasses many fields of research, I wasn’t too cl ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
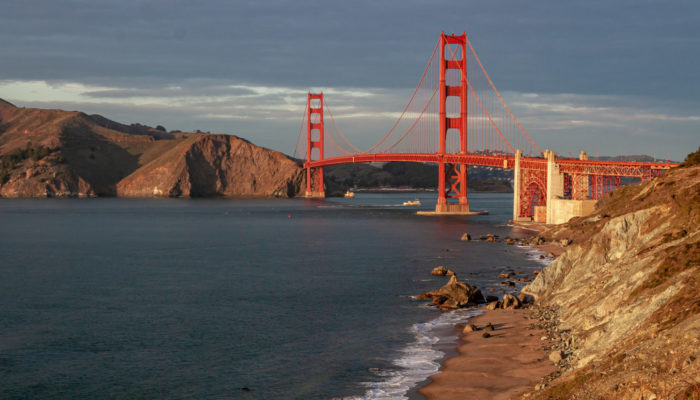
San Francisco: Where the Plates Meet
San Francisco has been a natural gathering place for people across the millennia. It is not a coincidence that this city, situated at the entrance to the largest estuary on the U.S. West Coast, owes its dramatic setting to active geology on the North American plate margin. The first people of the San Francisco Peninsula, the Ramaytush Ohlone, cared for the land here for thousands of years before E ...[Read More]
Cryospheric Sciences
Seafloor secrets: traces of the past Patagonian ice sheet
Today’s Patagonian ice caps are confined to the high-altitude Andean Mountain range as the Northern and Southern Patagonia ice fields, and they are rapidly melting. The southern part of the Patagonian ice cap drains partially through fast-flowing ice streams into the fjords of Patagonia. Glaciers in this region have been losing ice at accelerating rates by large calving events, due to rising globa ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
The Sassy Scientist – To Beer Or Not To Beer?
Theeerre ish noffink quite so dangerereroush as ashkink a seeeriouss question of scieeence at 18h30 on a Friday. Rudi inshtead ashks the not-at-all, definitely-not, who-me, ashking-for-a-friend queshtion: Can I get drunk at Friday Beers? Dear Rudi, Your question has more answers than asking a conference of geodynamicists what’s the best wine? With movement and beer restrictions in place, the ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
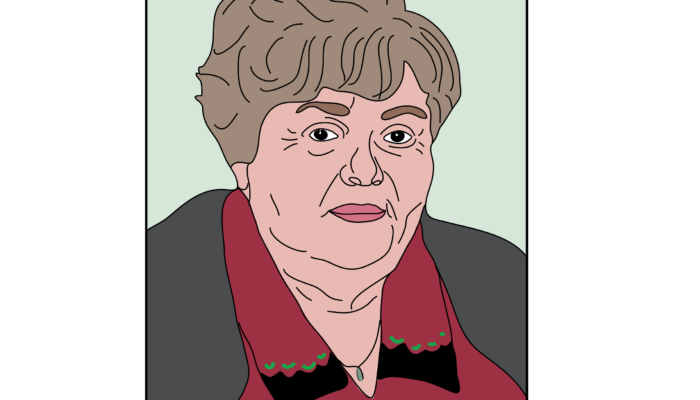
Franciszka Szymakowska (05/02/1927 – 2007): the woman whose drawings unraveled the geological history of the Carpathians
Franciszka Szymakowska was born on the 5th of February in 1927 in Krakow. She was lovingly known as “Niusia” (Antoni 2007). About her early life, not much is known. Franciszka did her studies at the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of the Jagiellonian University and graduated in 1952. During her studies, she started to work at the Polish Geological Institute. She remained affilia ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
Geodynamics 101: Dynamic Topography
The Geodynamics 101 series serves to showcase the diversity of research topics and/or methods in the geodynamics community. In this week’s post, Fred Richards explains how ‘Dynamic Topography’ is used in the Geosciences, and discusses the knowns, unknowns, and the challenges ahead. Since shortly after its tumultuous formation 4.5 billion years ago, Earth has been steadily cooling, wit ...[Read More]
Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology & Volcanology
#vEGU21 – Sessions in the Spotlight: Earthquake swarms and complex seismic sequences driven by transient forcing in tectonic and volcanic regions
The vEGU21 abstract submission is now open until 13 January 2021!! Every week from now on we will highlight a GMPV session on our blog to help you navigating your way through the wild jungle of almost 700 available EGU sessions! Today we will start our journey with session SM6.1: “Earthquake swarms and complex seismic sequences driven by transient forcing in tectonic and volcanic regionsR ...[Read More]