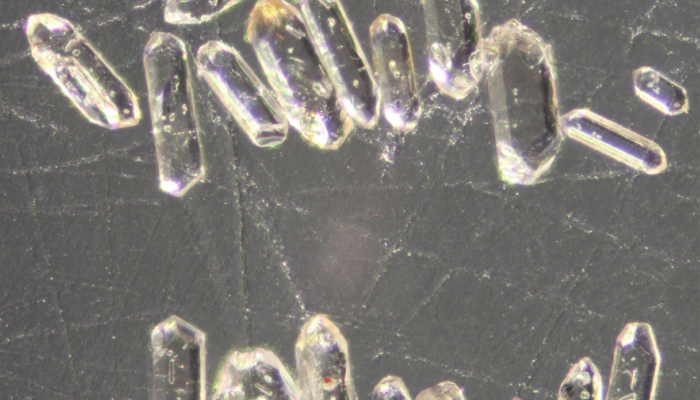
Name of proxy detrital zircon geochronology Type of record provenance proxy Paleoenvironment any sedimentary environment in a geologically diverse and diagnostic area Period of time investigated any Period of the geological timescale of the Earth, during which sedimentary deposits were formed How does it work? Igneous rocks form through assemblages of minerals crystallising from melt. While ...[Read More]
Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology & Volcanology
GMPV for Sustainable Development – Geothermal Energy
GMPV and The Sustainable Development Goals In 2015 all United Nations Member States adopted a set of Global Goals, as a universal call to protect our planet, end poverty and ensure that all people can enjoy peace and prosperity. These are called the Sustainable Development Goals – 17 integrated goals aimed at addressing the challenges our society is currently facing considering social, economic, a ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
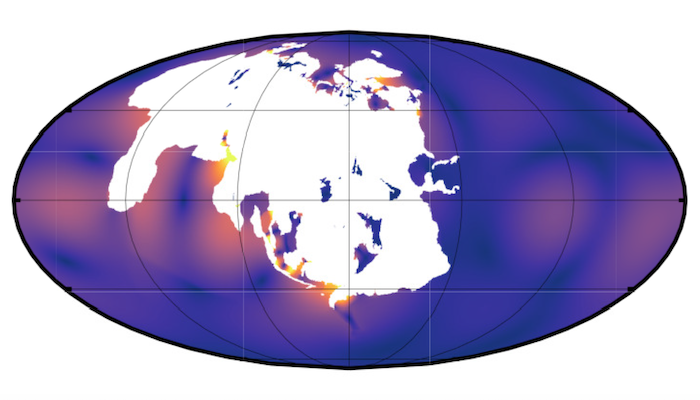
The Supercontinent Cycle
From orbital, to climatic, to tectonic evolution, many aspects of the Earth’s dynamics feature high degrees of cyclicity and episodicity, which can give us important insights into how the Earth’s works. The supercontinent cycle is an example capturing the Earth’s grandest scales and this week EGU geodynamics blog editor Tobias Rolf takes a closer look at it. Pangaea. This is a familiar term to eve ...[Read More]
Geomorphology
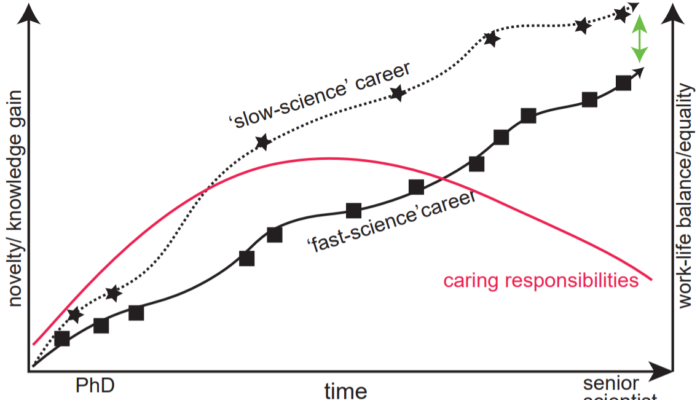
Slow versus fast science – summary and thoughts on the vEGU21 GM-ECS Great Debate
The Early career representatives of EGU’s Geomorphology Division (Andrea Madella (University of Tübingen), Annegret Larsen (Wageningen University), and Michael Dietze (GFZ – German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam)) organized the ECS-Great Debate on “Slow science versus fast science” at this year’s vEGU21 – edited by Sabine Kraushaar. – GM Guest bloggers: Annegret Larsen (Wag ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
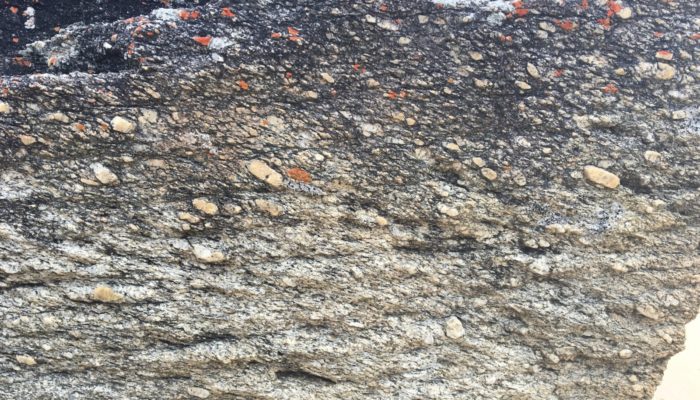
Features from the Field: S-C fabrics
As we have seen in previous Features from the field posts, structural fabrics are both informative and spectacular. But many structural geologists will list a shear zone fabric, such as mylonite, as their favourite! As Samuele, Hannah and I wrote in a previous post, shear zones are regions of intense deformation where rocks have accommodated an extremely high amount of strain and that strain has b ...[Read More]
Geodesy
Meet the new Geodesy Division President
Now that you know who the new ECS Reps are. Who else is part of the Geodesy Division Team? The outgoing president Johannes Böhm did an excellent job for the last four years. Now Annette Eicker has taken over in April as she was elected as the new president of the Geodesy Division. But who is Annette? We asked her a few questions about her work within the EGU, but also about her research and what s ...[Read More]
Natural Hazards
LANDAWARE: the international network on landslide early warning systems
For today’s interview, it gives me great pleasure to host Dr Manfred Stähli, who will tell us about a new initiative in the field of Landslide Early Warning Systems (LEWS), which is attracting the attention and participation of researchers from many countries. This initiative is called LandAware. Manfred is a senior scientist in mountain hydrology, slope stability and early warning systems a ...[Read More]
Stratigraphy, Sedimentology and Palaeontology
Podcast conversations about geology with researchers making key contributions to our understanding of the Earth and the Solar System
I have always sought to grasp the widest spatial and temporal context in which we find ourselves. So, after completing a physics degree at Cambridge University, I focused on cosmology and did a PhD on the structure of clusters of galaxies at Oxford University. I then joined the Science Museum, London, where I discovered the challenges and rewards of conveying science to the public. In 1984, The ...[Read More]
Cryospheric Sciences
Women of Cryo III: Women monitoring the Peruvian glaciers
The ruins of a hidden majestic city as Machupicchu in Peru immediately call for our attention. However, there are far more beautiful attractions found hidden amongst the landscape, such as the glaciers, high mountains or the cultural heritage in the area. In South America, glacial bodies are geographically restricted to the Andes, the mountain range that runs across the continent from the tropics ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
The Sassy Scientist – Video Versatility
Lis has been studying, investigating, deconvoluting, cross-correlating, referencing, inverting, plotting, database searching … and whatnot. With just a few synapses still firing at all cylinders and demonstrating an uninterrupted dispense of productivity, she wonders: Should I start my own (geodynamics…?) online video channel? Dear Lis, Why not? Everyone’s not working properly anyways in this day- ...[Read More]