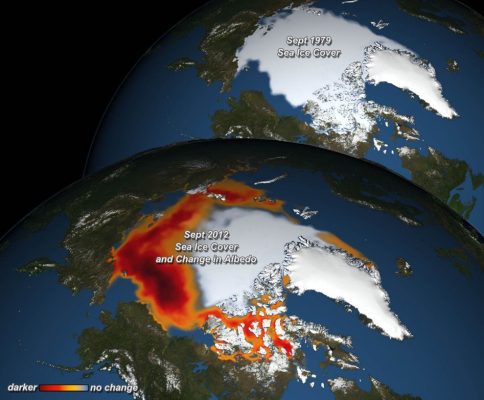
One of the most dramatic signals of Earth’s recent warming has been the precipitous decline of the Arctic sea ice. While the sea-ice decline is in response to warming ocean and atmosphere, it also has an important feed-back on the climate itself. Solar radiation and albedo Earth’s main energy source is solar radiation. This solar radiation is either absorbed in the atmosphere or at the ...[Read More]
Image of the week — The warming effect of the decline of Arctic Sea Ice