Wildfire – like the ones observed in the Northwest Territories, Canada in 2014 (Fig. 1) – is a natural part of permafrost landscapes, but fires are expected to get more frequent and severe as the climate warms. This could accelerate the degradation of permafrost, with negative consequences on the local and global scale! We have a pretty good understanding of how permafrost responds to fire t ...[Read More]
If you didn't find what you was looking for try searching again.
Natural Hazards
The bad, the good and the unpredictable: living with volcanoes / part 1
Introduction Humans have existed and lived alongside volcanoes for as long as we have been on the planet. For some, this has been beneficial and often, in fact, we can see how indigenous knowledge finds a sustainable approach living with them. However, in some cases, societies cannot cope and are overwhelmed with volcanic eruptions. There are many examples from archaeological studies dealing with ...[Read More]
Natural Hazards
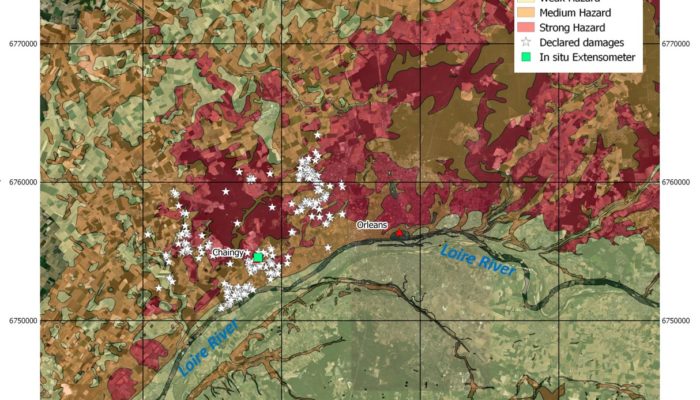
How can remote sensing and wavelet transform unravel natural and anthropogenic ground motion processes?
Underground energy storage and gas storage in aquifers In the context of energy transition, massive energy storage is a key issue for the integration of renewable sources into the energy mix. Storing energy in the underground can lead to larger-scale, longer-term and safer solutions than above-ground energy storage technologies. In particular, natural gas storages are designed to address different ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
Climate protests at the start of Global Week for Future
For months, students have skipped school on Fridays to ask for more action against climate change. To kick off the Global Week for Future, last Friday saw thousands of demonstrations in many countries around the globe, with not only high school students joining the fray, but people from all walks of life. GFZ Potsdam’s Bernhard Steinberger and Thilo Wrona share their experiences in Potsdam and Ber ...[Read More]
Atmospheric Sciences
A brighter future for the Arctic
This is a follow-up from a previous publication. Recently, a new analysis of the impact of Black Carbon in the Arctic was conducted within a European Union Action. “Difficulty in evaluating, or even discerning, a particular landscape is related to the distance a culture has traveled from its own ancestral landscape. As temperate-zone people, we have long been ill-disposed toward deserts and ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
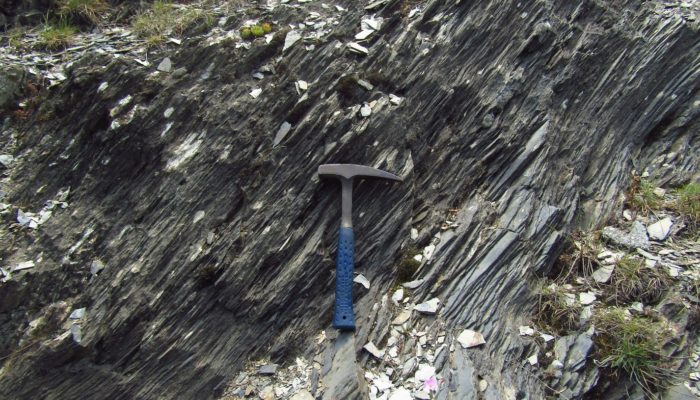
Features from the field: Foliation
Have you ever walked on a mountain trail, passing past outcrops of rocks and noticed that many rocks appear to be split along a well-defined orientation? If you have, you might have seen one of the most important structures in metamorphic rocks – called foliation. The term ‘foliation’ derives from the Latin folium, meaning ‘leaf’. A rock with a foliation looks like a pile of R ...[Read More]
WaterUnderground
Quest for Sustainability of Heavily Stressed Aquifers at Regional to Global Scales: Upcoming Chapman Conference
Abstracts are due soon (July 10th) for the upcoming Chapman conference on groundwater sustainability on Oct 21-24, 2019 in Valencia, Spain. Hopefully this will be a rare opportunity where many of the leading people on groundwater sustainability will gather with a shared intention to share, discuss and debate scientific advances and encourage a pivot towards groundwater sustainability. A range of p ...[Read More]
Hydrological Sciences
Featured catchment series: The North is not forgotten!
This is the first post of “Featured Catchment”, a series of posts in the HS Blog that present experimental catchments across Europe and beyond. Here, the authors of the posts will explain the main characteristics (e.g., climate, geology, topography, land use) of their catchments, why hydrologic research is important in their study areas, describe the applied methodologies (field instrumentation an ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
Minds over Methods: The faults of a rift
Do ancient structures control present earthquakes in the East African Rift? Åke Fagereng, Reader in Structural Geology, School of Earth and Ocean Sciences, Cardiff University For this edition of Minds over Methods, we have invited Åke Fagereng, reader in Structural Geology at the School of Earth and Ocean Sciences, Cardiff University. Åke writes about faults in the Malawi rift, and the seismic ha ...[Read More]
GeoLog
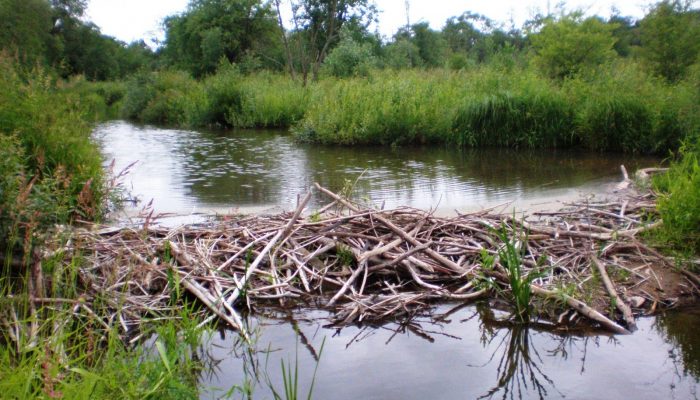
Could beavers be responsible for long-debated deposits?
Following her presentation at the European Geosciences Union General Assembly in Vienna, I caught up with geomorphologist and environmental detective Annegret Larsen from the University of Lausanne, Switzerland, about beavers, baffling sediments and a case she’s been solving for the past seven years. Back in 2012 the German geomorphology community was seriously debating the source of buried black ...[Read More]

![For Dummies – How do wildfires impact permafrost? [OR.. a story of ice and fire]](https://blogs.egu.eu/divisions/cr/wp-content/blogs.dir/17/files/2019/10/DJI01011-700x400.jpg)