When we think of Earth’s rotation, it is tempting to imagine a perfectly smooth spin. But in reality, Earth’s rotation is irregular and dynamic, and is influenced by forces inside and outside of our planet. To describe the changing orientation of the Earth in space over time Earth Orientation Parameters (EOPs) are measured with fundamental geodetic measuring techniques, e.g., Very Long Baseline In ...[Read More]
Bits and Bites of Geodesy – Satellite altimetry: What else can we do with it?
In the previous post of this series, we learned how we can use satellite radar altimetry to retrieve highly accurate estimates of global sea level changes. If only reading “sea level” triggers your climate anxiety – we got you covered! In this post we will introduce you to three more applications of radar altimetry, where the first two are not directly connected to climate change. Instead, w ...[Read More]
High resolution terrestrial water storage changes from combination of GRACE and models
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission (2002-2017) consisted of two satellites at ~500 km altitude separated by 200 km, following each other in the same orbit. The distance between the two GRACE satellites changes because of the gravitational pull of the masses beneath the satellites. As such, mass changes at or near the Earth’s surface caused variations in the dista ...[Read More]
Calculating postglacial sea-level change within few seconds: a statistical emulator for GIA
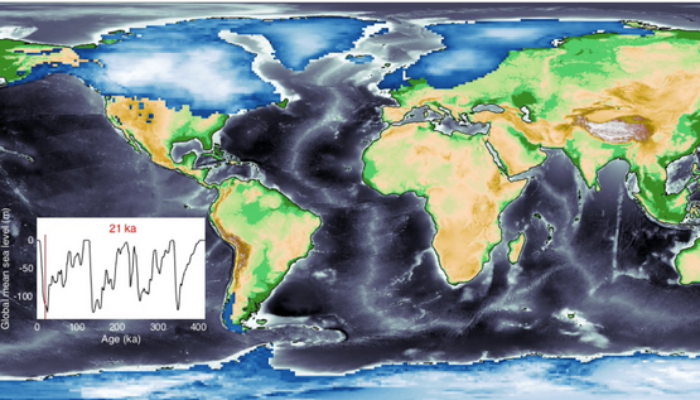
Sea-level change serves as a direct indicator of climate change with profound implications for coastal areas. Since 1900, the global mean sea level (GMSL) has risen over 20 cm, leading to beach erosion, delta inundation, and increased flooding worldwide. Over glacial cycles spanning tens of thousands of years, interactions between ocean and continental-scale ice sheets can cause GMSL to fluctuate ...[Read More]



