On 22 March 2018, large amounts of Saharan dust were blown off the Libyan coast to be further deposited in the Mediterranean, turning the usually white snow-capped Mountains of Turkey, Romania and even Caucasus into Martian landscapes. As many people were struck by this peculiar color of the snow, they started documenting this event on social media using the “#orangesnow hashtag”. Instagram and t ...[Read More]
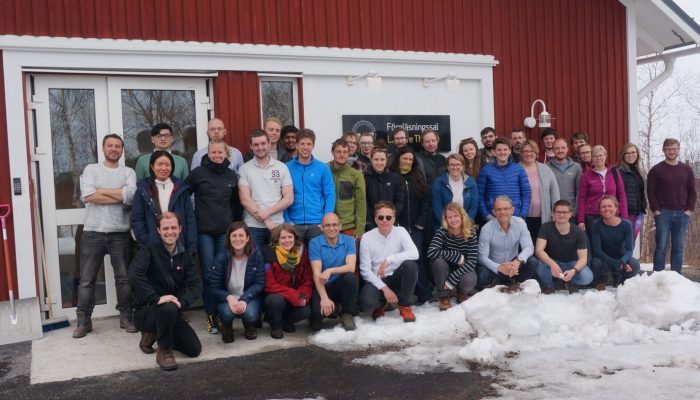
Image of the Week – Polar Prediction School 2018
Early career scientists studying polar climate are one lucky group! The 29 young scientists who took part in the 10 day Polar Prediction School this year were no exception. They travelled to Arctic Sweden to learn and discuss the challenges of polar prediction and to gain a better understanding of the physical aspects of polar research. The Year of Polar Prediction The Year of Polar Prediction (YO ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Antarctica: A decade of dynamic change
Whilst we tend to think of the ice flow in Antarctica as a very slow and steady process, the wonders of satellites have shown over the last two decades it is one of the most dynamic places on Earth! This image of the week maps this dynamical change using all the satellite tools at a scientist’s disposal with novel statistical methods to work out why the change has recently been so rapid. Why do ...[Read More]
Image of the Week — Biscuits in the Permafrost
In Svalbard, the snow melts to reveal a mysterious honeycomb network of irregular shapes (fig. 1). These shapes may look as though they have been created by a rogue baker with an unusual set of biscuit cutters, but they are in fact distinctive permafrost landforms known as ice-wedge polygons, and they play an important role in the global climate. Ice-wedge polygons: Nature’s biscuit-cutter In wint ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Cure from the Cold?
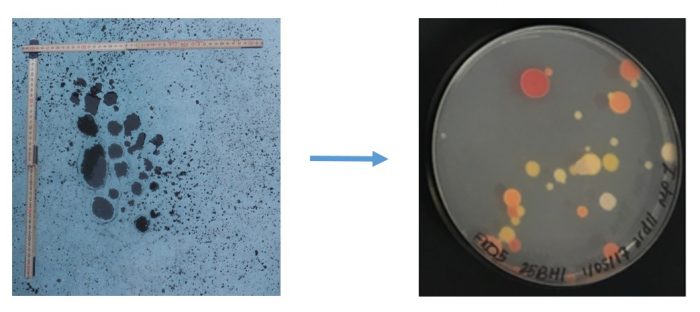
Humans rely on antibiotics for survival, but over time they are becoming less effective. So-called ‘superbugs’ are developing resistance to our most important drugs. The key to this global issue may be found in the cryosphere, where extreme microbiologists are hunting for new compounds in the cold that could help us win the war against antimicrobial resistance. Discovering drugs in Earth’s coldest ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Why is ice colourful?
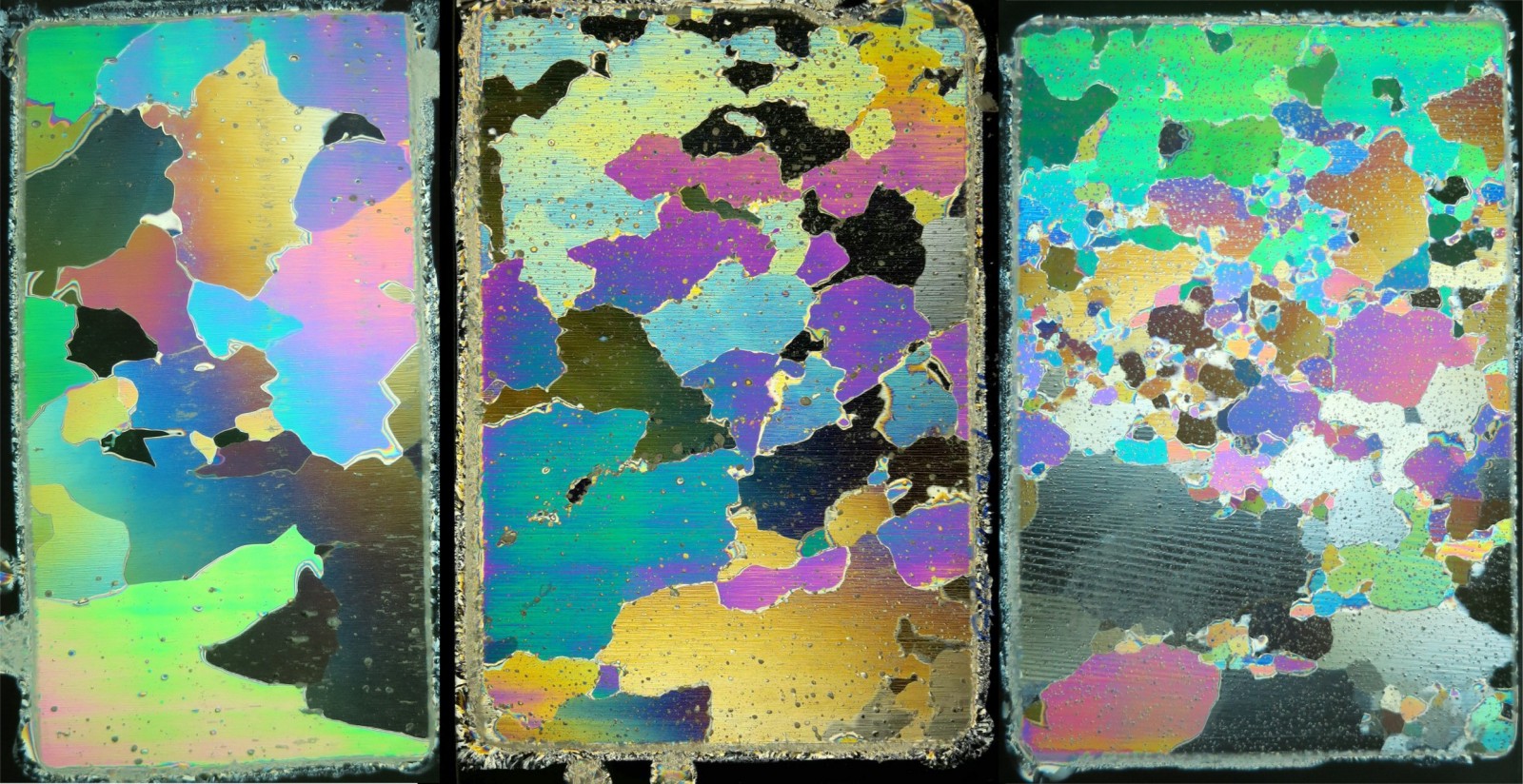
When you think of glacier ice, what colour first springs to mind? Maybe white, blue or transparent? Well, glacier ice can, in fact, be mesmerising and multi-coloured! Our image of the week shows thin sections of glacier ice under polarised light. These sections were cut from block samples of two Alpine glaciers in Switzerland (Chli Titlis and Grenzgletscher). In these images the individual ice c ...[Read More]
Image of the week — Making pancakes
It’s pitch black and twenty degrees below zero; so cold that the hairs in your nose freeze. The Arctic Ocean in autumn and winter is inhospitable for both humans and most scientific equipment. This means there are very few close-up observations of sea ice made during these times. Recently, rapidly declining coverage of sea ice in the Arctic Ocean due to warming climate and the impending likelihood ...[Read More]
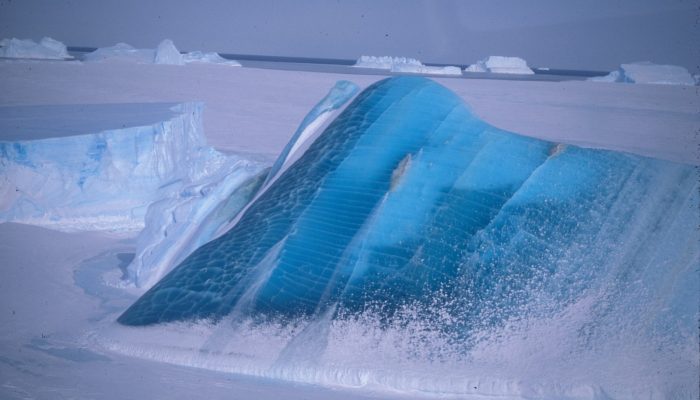
Image of the Week – Super-cool colours of icebergs
It is Easter weekend! And as we do not want you to forget about our beloved cryosphere, we provide you with a picture nearly as colourful as the Easter eggs: very blue icebergs! What makes them so special? This is what this Image of the Week is about… What are icebergs made of? Icebergs are chunks of ice which break off from land ice, such as glaciers or ice sheets (as you’ll know if you rem ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Geothermal heat flux in Antarctica: do we really know anything?
Geothermal heat flux is the major unknown when we evaluate the temperature and the presence/absence of water at the bed of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. This information is crucial for the Beyond Epica Oldest Ice project, which aims to find a continuous ice core spanning 1.5 million years (see this previous post). A lot of work has been done* to determine geothermal heat flux under the entire Antarctic ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – Broccoli on Kilimanjaro!
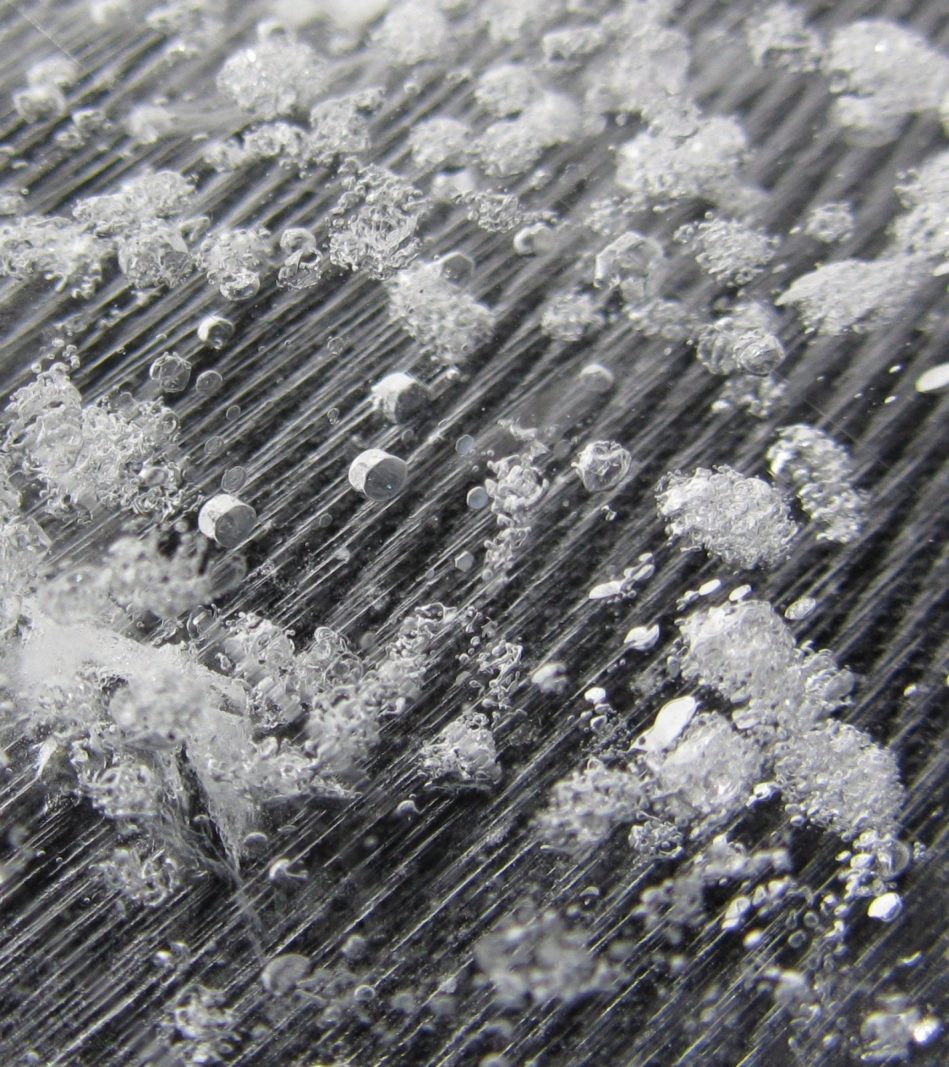

On the plateau of Kilimanjaro, Tanzania, the remnants of a glacier can be found and the ice from that glacier contains a rather interesting feature – Broccoli! Not the vegetable, but bubbles that look a lot like it. Our Image of the Week shows some of these strange “Broccoli Bubbles”. Read on to find out more about where these were found and how we can see them. There is not much ice left on the m ...[Read More]


