Numerical models are omnipresent in climate research. Constructed to understand the past, to forecast future climate and to gain new knowledge on natural processes and interactions, they enable the simulation of experiments at otherwise unreachable time and spatial scales. These instruments have long been considered to be fed – let even determined – by either theories or observations alone. ...[Read More]
Magnetic minerals: storytellers of environmental and climatic conditions
Name of proxy Environmental Magnetism (also known as enviromagnetics) Type of record Environment and climate proxy Paleoenvironment Sedimentary environments (for the most part) Period of time investigated Present times to millions of years (depending on the preservation conditions) How does it work? Magnetism is a physical property that results from the behaviour of elementary particles in any sub ...[Read More]
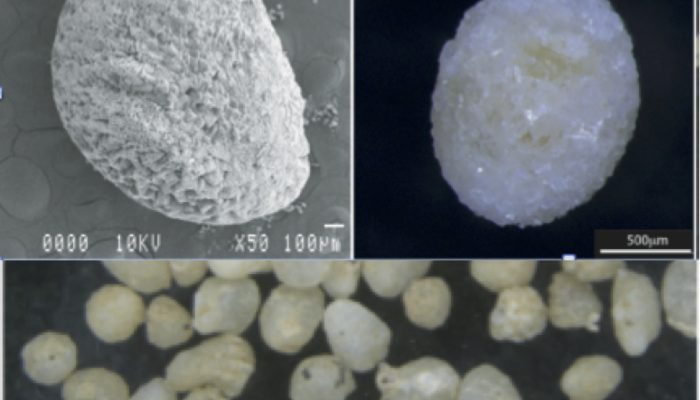
How earthworms can help us understand past climates?
Name of proxy Earthworm calcite granules (ECG) Type of record Paleotemperature and paleoprecipitation reconstruction; radiocarbon dating Paleoenvironment Continental environments – loess/paleosol sequences Period of time investigated Mostly Last full Glacial cycle – from 112,000-15,000 years Before Present (BP) (or older depending on the preservation of the granules). How does it work? Earth ...[Read More]
God does not play DICE – but Bill Nordhaus does! What can models tell us about the economics of climate change?
Climate change has been described as “the biggest market failure in human history”[1]. Although fuel is costly, emitting the by-product CO2 is for free; yet it causes damages to society. In other words, those who benefit, by using the atmosphere as waste dump, do not pay the full costs, i.e. the adverse effects climate change has on societies on a global scale. Can this market failure be cured? Sh ...[Read More]