The Indian subcontinent is situated in Southern Asia, where it projects southwards from the Himalayas into the Indian Ocean. Along the northern border of this subcontinent, the Himalayas – home to the earth’s highest mountains on land – stretch with a length of ~2500 km and a width of 300 km. The stunning mountain ranges of the Himalayas provide a considerable physical barrier for air masses from/ ...[Read More]
Introducing the TIMES initiative
TIMES is the acronym of a large-scale international science initiative “Time Integrated Matrix for Earth Sciences” (Link: https://www.codd-home.net/times/). The idea is to launch a global program with the aim of synchronizing age models for particularly important geological climate records from the past 100 million years. The motivation for this program is given in a white paper published in the j ...[Read More]
The Deep Dust project continues!
In 2019, the EGU SSP blog reported from a workshop exploring Paleozoic dust. By now, the Deep Dust initiative is supported by the International Continental Scientific Drilling program, which is an important step. It is planned to drill in the US in a first project phase. The Deep Dust Drilling Project (DEEP DUST) is focused on understanding paleoclimatic conditions, biospheric responses and climat ...[Read More]
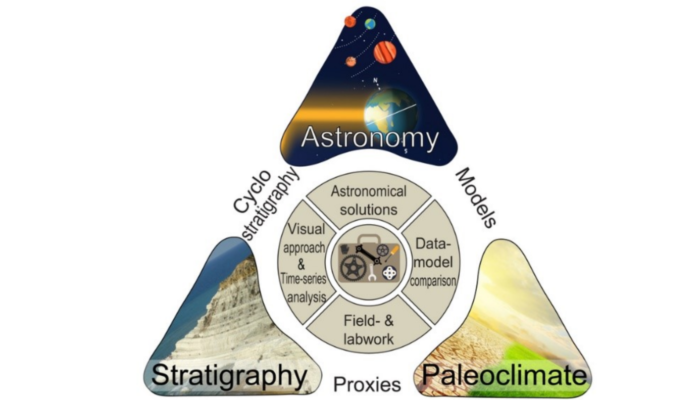
An online learning platform for cyclostratigraphy – www.cyclostratigraphy.org
Cyclostratigraphers aim to read and understand the effect of climate-driven orbital changes in the geological record through time. In doing so, they start from an important prerequisite: An imprint of insolation variations caused by Earth’s orbital eccentricity, obliquity and/or precession (Milankovitch forcing) can be preserved in the geological rock record. The new www.cyclostratigraphy.org webs ...[Read More]