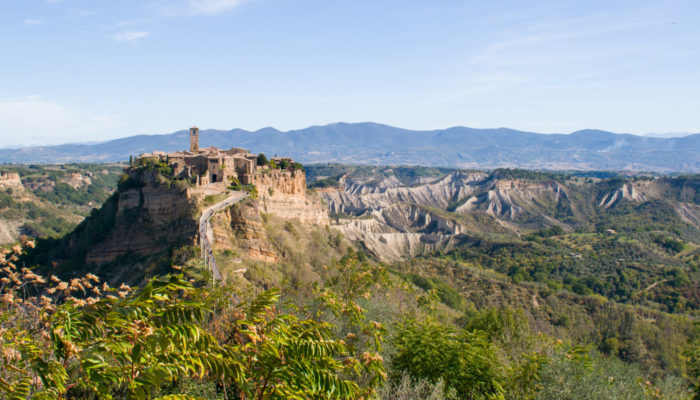
On top of a steep cliff standing out from the surrounding countryside, lies the small town of Civita di Bagnoregio, one of the most famous villages of Italy. It is often called the dying town, although more recently people have started to refer to it as fighting to live. What this little town is fighting against is the threat of erosion, as its walls are slowly crumbling down. Located in central I ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
The Role of Geosciences in Exoplanet Science
How can geoscience methods be incorporated into the research of extrasolar planets? These are planets that are beyond our own solar system and their geological properties are mostly unknown. Kaustubh Hakim is a postdoctoral researcher at the Center for Space and Habitability in Bern, Switzerland where he studies the interiors of rocky exoplanets and geochemical cycles using theory and lab experime ...[Read More]
Hydrological Sciences
SciArt & Hydrology: how about having an art exhibition as part of your hydrology PhD thesis?
On November 1st 2019, Louise Arnal, a PhD candidate at the University of Reading and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), had her art exhibition opening event at The Museum of English Rural Life (Reading, UK). This exhibition was part of her PhD thesis on hydrology, and was called “Gambling with floods?” For me, it was the first time I saw a PhD thesis in hydrology that ...[Read More]
Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology & Volcanology
#EGU2022 Sessions in the Spotlight: GMPV1.3, Advances in microanalysis: Insights into nanoscale trace element heterogeneities
One of the great things about geology is how it incorporates observations from the huge to the tiny. We can think on the scale of whole earth (or even bigger), continents, regions, outcrops, rocks, crystals or atoms, and everything in between. If you are in the latter groups, you are probably following closely the amazing developments in microanalysis that seem to happen every year, allowing us to ...[Read More]
Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology & Volcanology
#EGU2020 Sessions in the Spotlight: GMPV2.3: The relationship between slab dehydration, mantle wedge processes and subduction zone geodynamics
Now that we are 6 weeks out from the EGU2020 abstract deadline, it’s a great time to choose your session and write an abstract! Because, lets be honest, nobody wants to be writing an abstract over the Christmas holidays… Every few days, we will be highlighting a session in the Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology and Volcanology section, to help make your session choice as easy as possi ...[Read More]
Solar-Terrestrial Sciences
Chasing solar storms as an early career scientist
Hello! My name is Erika Palmerio and I am a newly qualified Dr in space physics from the University of Helsinki, Finland. In this blog post I will talk about my PhD research and my future career plans. The title of my PhD dissertation is “Magnetic structure and geoeffectiveness of coronal mass ejections”. Coronal mass ejections (or CMEs) are huge and spectacular clouds of magnetic field and plasma ...[Read More]
Cryospheric Sciences
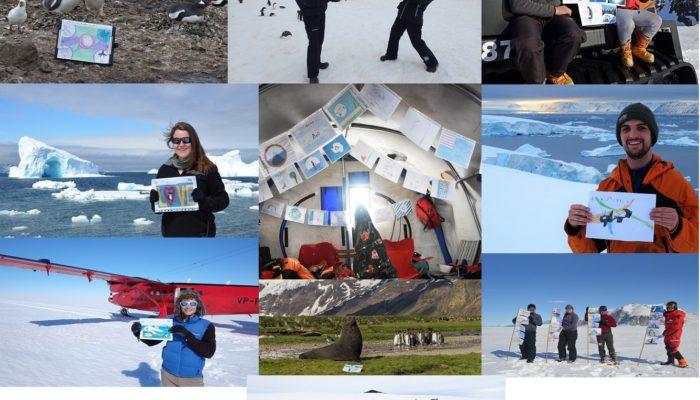
Did you know…? Antarctica Day 2019 – 60 years of peace
December 1st 2019 marks the 60th anniversary of the signing of the Antarctic treaty. To celebrate the signing of the treaty, ‘Antarctica Day’ now occurs each year on December 1st. But what is the Antarctic Treaty? How do people celebrate? This week’s blog post will tell you everything you need to know, just in time for celebrations! Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty was originally signed by 12 ...[Read More]
Geodynamics
The Sassy Scientist – A Tale Of Two Offices
Every week, The Sassy Scientist answers a question on geodynamics, related topics, academic life, the universe or anything in between with a healthy dose of sarcasm. Do you have a question for The Sassy Scientist? Submit your question here or leave a comment below. It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness. Lucie lives through thos ...[Read More]
Seismology
Seismology Job Portal
On this page we regularly update open positions in Seismology. Do you have a job on offer? Contact us at ecs-sm@egu.eu
Nonlinear Processes in Geosciences
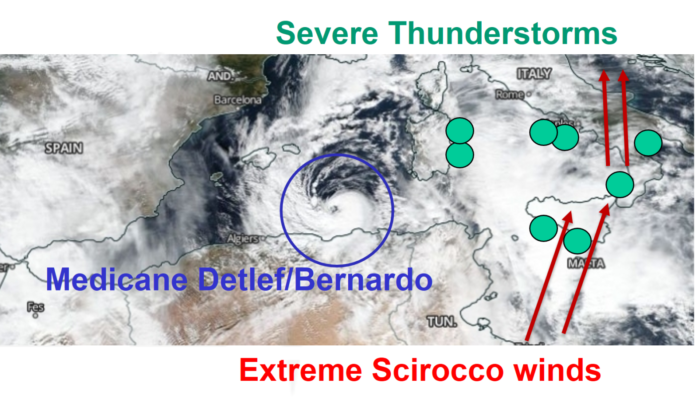
Medicanes, thunderstorms and Acqua Alta in Venice: what is the role of climate change?
A Mediterranean cyclone, high tides and climate change: these three ingredients made the 12/11/2019 acqua alta event in Venice exceptional. This combination of causes determined what climate scientists define as a compound extreme event, a non-linear mix of factors which led to several and connected extreme weather phenomena in the Mediterranean area. Let us start by the analysis of the atmospheri ...[Read More]