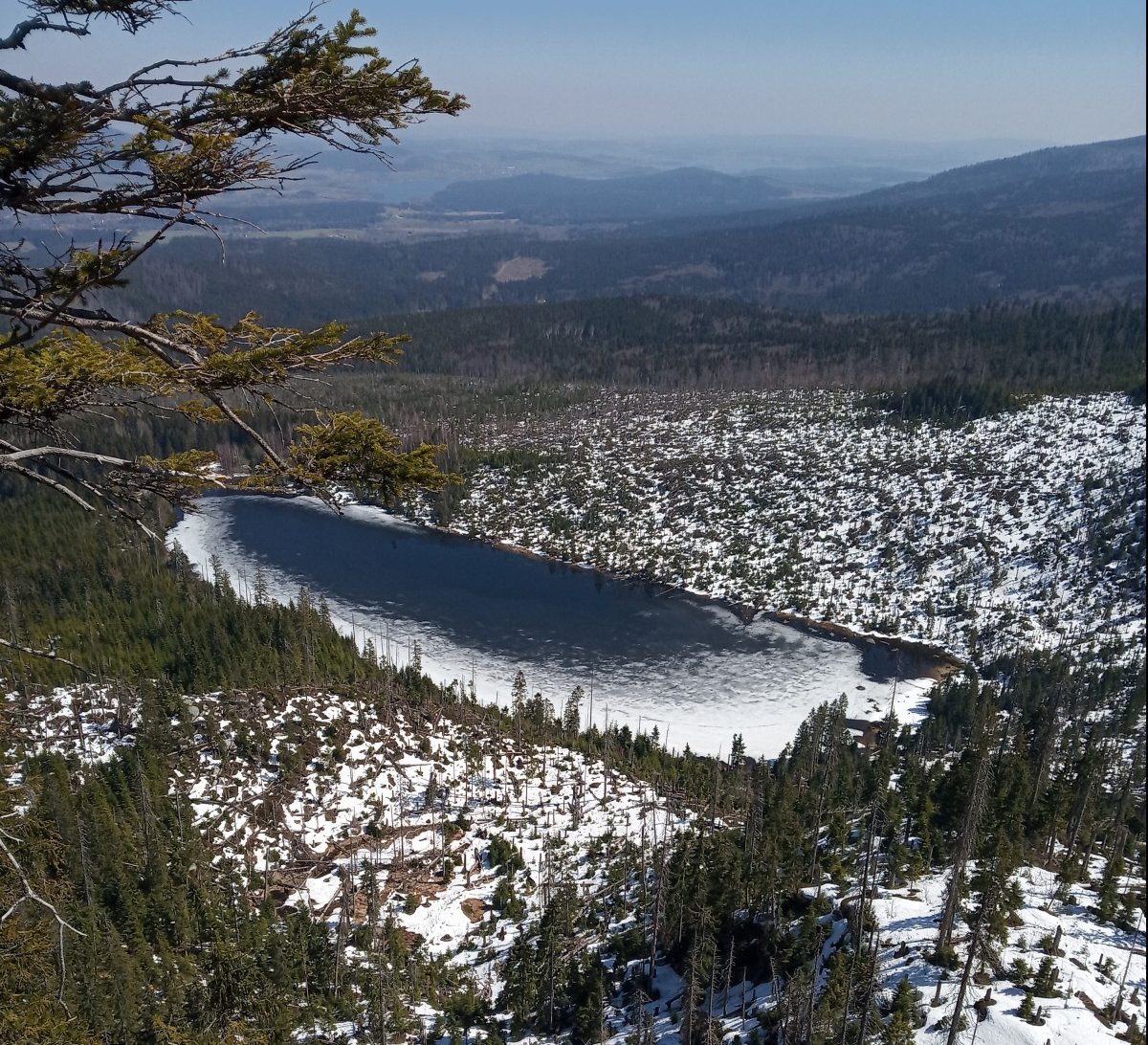
Melting snowfields in a forested catchment of glacial lake in Šumava (mid-April), the Czech Republic [Credit: Lenka Procházková]
The new snow melting season has just started in the mountains of Europe and will last, in many alpine places, until the end of June. Weather in the middle of April is changeable. In the last few days sub-zero air temperatures have prevailed in the mountains during the day. In a frame of an international research project, me (Charles University) and Daniel Remias (Applied University Upper Austria), are both packing warm winter clothes as well as all the research equipment necessary for a new field mission: the aims are to find blooming spots of snow algae and to collect it for analyses. Upon our arrival in Šumava, a surprising but wonderful sunny day welcomes the expedition and we regret not taking the sun cream with us. While we are walking on still-compact partly frozen snowfields, our heads feel that they are exposed to hot summer.
Snow blooms – what do they look like?
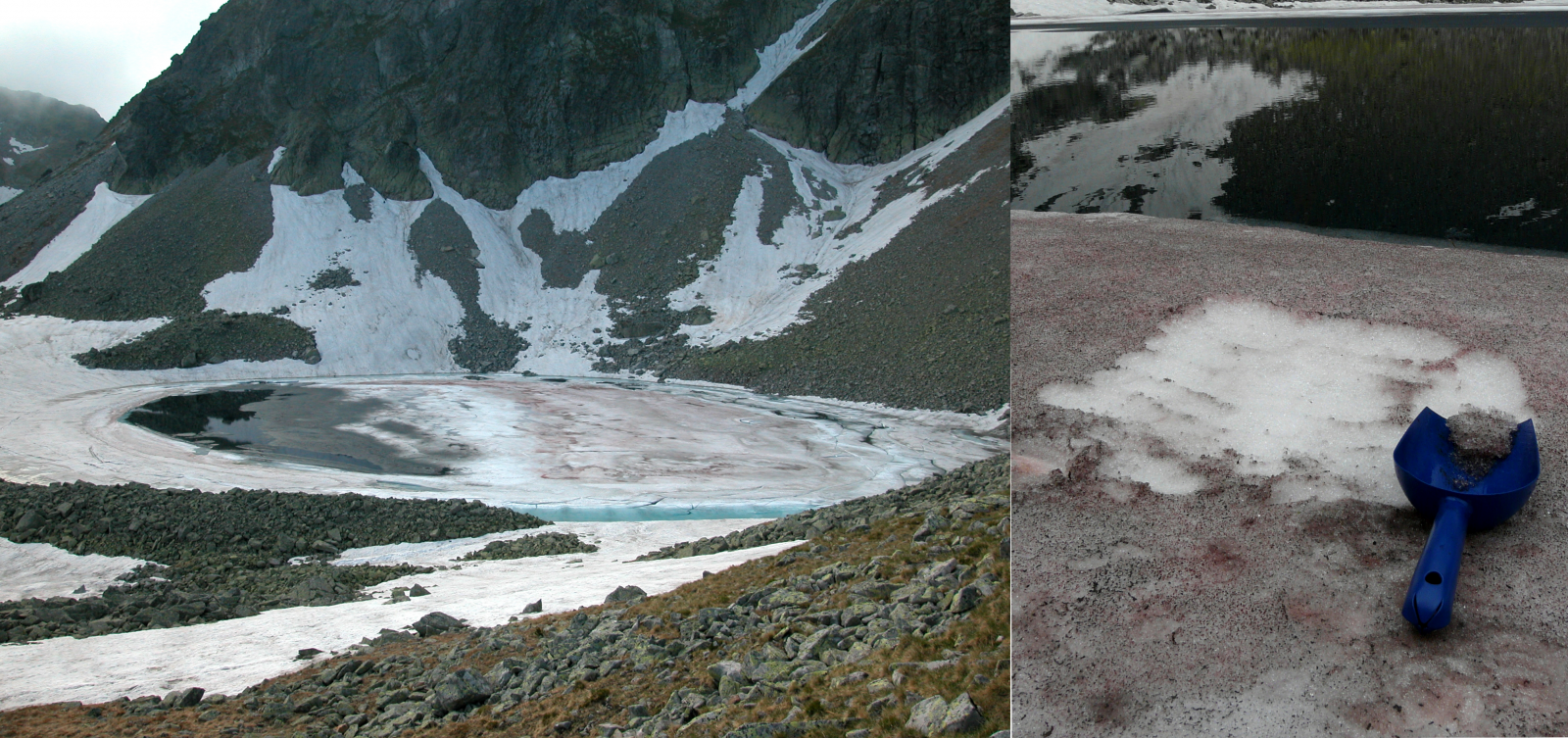

Red snow colouration at nearly all ice-covered parts of a high-alpine glacial lake (mid-June), High Tatras (Slovakia). Detailed view of red snow after harvest [Credit: Daniel Remias and Lenka Procházková, see study Procházková et al. 2018a]
Snow blooms – see the figure above – can be found in polar and alpine regions worldwide. Availability of liquid water is a key factor for the development of a snow algae population. In our experience, only wet and slowly melting snowfields are suitable. This colourful phenomenon can appear in different colour shades, as green, yellow, pink, orange or blood-red (Procházková et al., 2018a). Snow blooms are currently a focus of an increasing number of studies because of their significant effects on albedo reduction and subsequent acceleration of snow and ice melting.
Why are they colourful?
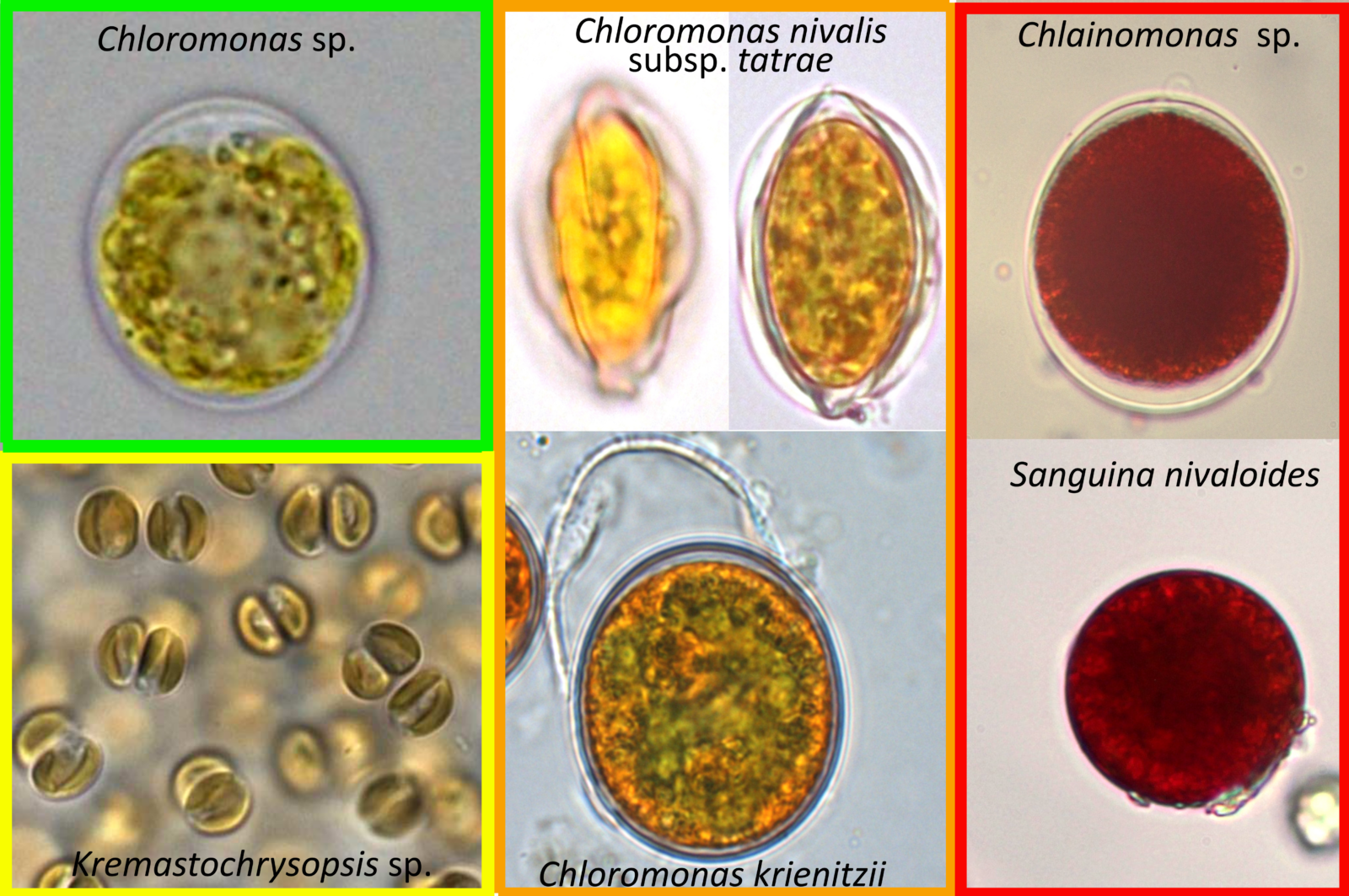
A few representatives of microalgae forming blooming snow – a coloured frame of each of these species corresponds with a colour of blooming snowfields [Credit: Lenka Procházková and Daniel Remias]
The macroscopic blooms are caused by microalgae of a cell size ranging from ~5 µm up to ~100 µm. During the melting season, cells live in a water film microhabitat surrounding large snow grains. The main genera that form these blooms are Chloromonas, Sanguina and Chlainomonas, each associated with a specific bloom color (see the figure above). A massive population development of golden algae can also occur.
When in the season do blooms occur?
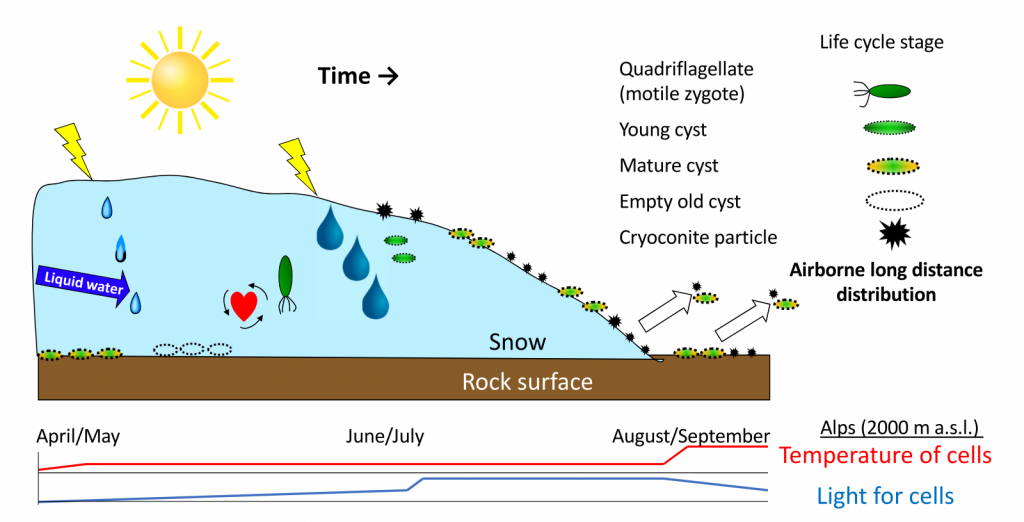
Typical seasonal life cycle of a snow alga (Chloromonas nivalis), based on observation over many seasons in European Alps [Figure modified with permission from Sattler et al. 2010]
I would like to reveal a few secrets of snow algae.
The first strategy represents their seasonal life cycle. At the beginning the season in late April, one can hardly see any snow colouration. Snow algae from the previous seasons are lying at the interface between snow and soil in a resistant stage (called cyst). Snow is starting to melt slowly, and the cysts recognize the availability of liquid water and germinate. Flagellates are released and migrate upwards to the sub-surface layers, where they mate. With proceeding melting the cysts are accumulated and exposed at the snow surface. After total snowmelt these resistant stages should survive over summer in soil or at bare rock, where they can be subject to long-distance transport by wind.
The red colour of snow is caused by astaxanthin
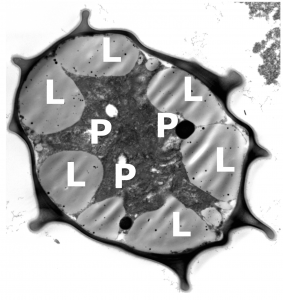
A cross-section of a typical snow algal cyst, Chloromonas nivalis-like species, with abundant lipid bodies (“L”) with astaxanthin and plastids (“P”) [transmission electron microscope, credit: Lenka Procházková]
The next strategy of snow algae is an accumulation of the red pigment astaxanthin during their maturation, which has many benefits to life of these microorganisms. For example, astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant, and its synthesis is not limited by the supply of nitrogen.
Another big advantage of astaxanthin is its protective action against excessive visible and harmful ultraviolet irradiation which are characteristic for snow surfaces in alpine and polar regions. This “sunscreen” effect of astaxanthin – which has maximum absorbance in the visible light region and also a significant capability of UV protection – is supported by the algae’s clever intracellular arrangement (shown in the figure above), namely that sensitive compartments of the algae, like chloroplast or nucleus, are located in the central part, whereas lipid bodies, which accumulate the astaxanthin, are in the periphery.
Our mission
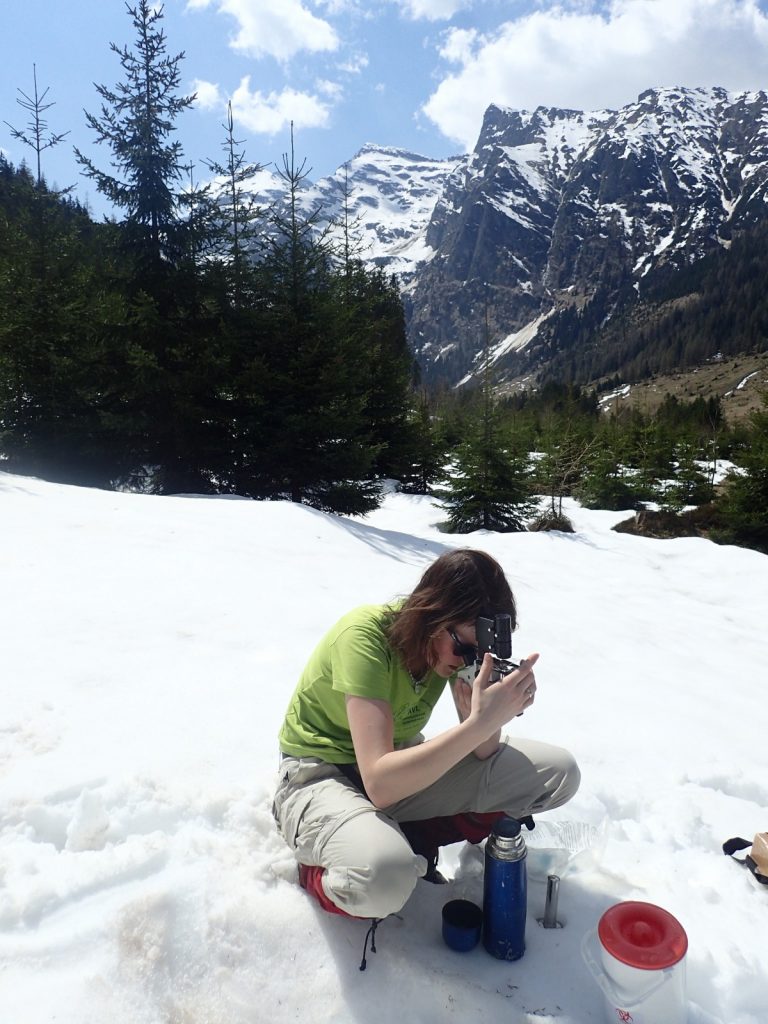

Sequence-related sampling in Lower Tauern, Austria. Checking of a qualitative composition of a sampled spot using light microscope already in field. [Credit: Linda Nedbalová]
Do you wonder why we explore the physiology and biodiversity of snow algae? Because these extremophilic organisms cope with high ultraviolet radiation, repeated freeze-thaw cycles, desiccation, mechanical abrasion, limited nutrients and short season and are well adapted to it! Because of their ability to adapt to these extreme conditions, pigments of snow algae (as the astaxanthin presented above) are even used as biomarkers to detect life on Mars! Moreover, these microalgae are essential primary producers in such an extreme ecosystem, where phototrophic life is restricted to a few specialised organisms. For instance, they provide a basic ecosystem for snow bacteria, fungi and insects. Snow algae communities play an important role in supraglacial and periglacial snow food webs and supply nutrients that will be delivered throughout the glacial ecosystem.
Further reading
- Lutz et al. (2016) The biogeography of red snow microbiomes and their role in melting arctic glaciers.
Nature Communication - Procházková et al. (2018) Chloromonas nivalis subsp. tatrae, subsp. nov. (Chlamydomonadales, Chlorophyta): re-examination of a snow alga from the High Tatra Mountains (Slovakia). Fottea
- Remias et al. (2018) Ecology, cytology and phylogeny of the snow alga Scotiella cryophila K-1 (Chlamydomonadales, Chlorophyta) from the Austrian Alps. Phycologia
- Segawa et al. (2018) Bipolar dispersal of red-snow algae. Nature Communication
Edited by Jenny Turton
Lenka Procházková is a PhD Student at the Charles University, Prague, the Czech Republic. She investigates biodiversity and ecophysiology of snow algae. Her favourite algal group is in her focus in a lab as well as in field samplings in the European Alps, High Tatras, Krkonoše, Šumava and Svalbard. Contact Email: lenkacerven@gmail.com