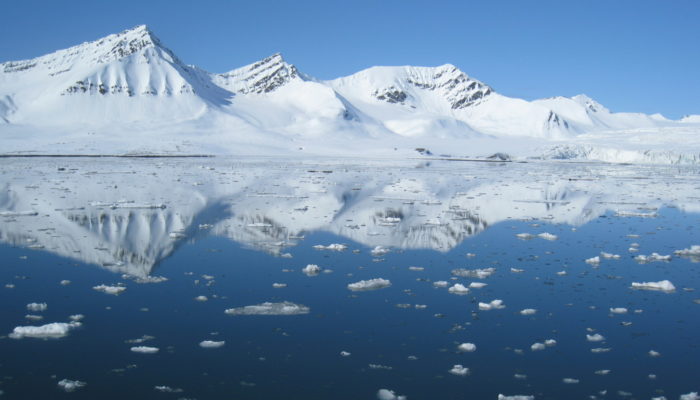
More than 11 years ago, I joined the Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain) in Belgium as a teaching assistant. The 2007-2009 International Polar Year (IPY), a worldwide collaborative effort aiming at better understanding our polar regions, had just finished, and the scientific community was concerned about the sudden drop in the summer Arctic sea ice extent that had occurred two years befor ...[Read More]
Generation #polarprediction