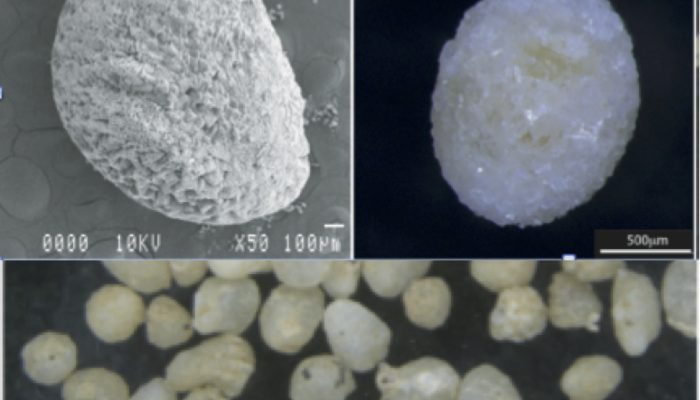
Name of proxy Earthworm calcite granules (ECG) Type of record Paleotemperature and paleoprecipitation reconstruction; radiocarbon dating Paleoenvironment Continental environments – loess/paleosol sequences Period of time investigated Mostly Last full Glacial cycle – from 112,000-15,000 years Before Present (BP) (or older depending on the preservation of the granules). How does it work? Earth ...[Read More]
God does not play DICE – but Bill Nordhaus does! What can models tell us about the economics of climate change?
Climate change has been described as “the biggest market failure in human history”[1]. Although fuel is costly, emitting the by-product CO2 is for free; yet it causes damages to society. In other words, those who benefit, by using the atmosphere as waste dump, do not pay the full costs, i.e. the adverse effects climate change has on societies on a global scale. Can this market failure be cured? Sh ...[Read More]
What can artificial intelligence do for climate science?
What is machine learning? Artificial Intelligence, and its subfield of machine learning, is a very trending topic as it plays an increasing role in our daily life. Examples are: translation programs, speech recognition software in mobile phones and automatic completion of search queries. However, what value do these new techniques have for climate science? And how complicated is it to use them? Th ...[Read More]
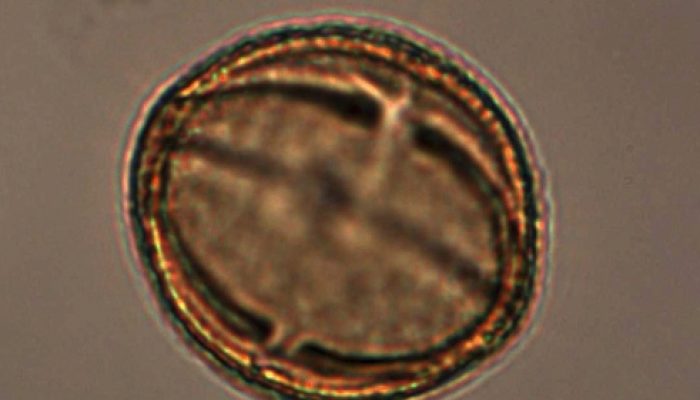
Pollen, more than forests’ story-tellers
Name of proxy Sporomorphs (pollen grains and fern spores) Type of record Biostratigraphy and Geochronology markers, Vegetation dynamics Paleoenvironment Terrestrial environment Period of time investigated Present to 360 million years How does it work? The sporomorphs (pollen grains and fern spores) are cells produced by plants involved in the reproduction. They are microscopic (less than a fifth o ...[Read More]