It’s I’m a Geoscientist week! Or more exactly: weeks. From March 9 until March 20, the EGU supports I’m a Geoscientist to help students engage with scientists about real science. The Energy, Resources and Environment Division of the European Geosciences Union encompasses a broad range of different ERE-related topics, from surface to subsurface, spanning all aspects of geosciences. In order to demonstrate how broad the Division actually is, and what you can do as a geoscientist to be involved with energy, resources or the environment, we asked the members of the ERE committee to introduce themselves and explain how their day-to-day work relates back to ERE.
Today our Deputy President Michael Kühn, currently working at GFZ, the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam, will explain how his work touches upon most of the topics involved with ERE!
***
 The ERE division of the EGU contributes finding answers to the questions of how to provide adequate and reliable supplies of affordable energy and other resources for humankind obtained in environmentally sustainable ways. Every year this is reflected in our programme for the General Assembly. We cover topics like wind and solar power, geothermal energy, biomass, geological CO2 storage and others. My own work fits nicely into this framework because as chemist and hydrogeologist I look for solutions in the controversial area of Energy, Resources and the Environment.
The ERE division of the EGU contributes finding answers to the questions of how to provide adequate and reliable supplies of affordable energy and other resources for humankind obtained in environmentally sustainable ways. Every year this is reflected in our programme for the General Assembly. We cover topics like wind and solar power, geothermal energy, biomass, geological CO2 storage and others. My own work fits nicely into this framework because as chemist and hydrogeologist I look for solutions in the controversial area of Energy, Resources and the Environment.
Prevention and remediation for groundwater protection is important. Therefore sustainable and responsible management of groundwater resources must be given utmost priority to avoid water crises and water conflicts. Here, the utilization of geo-resources in deep groundwater systems is of great importance, because it can always have an effect on the shallow groundwater systems. In many areas, salt and fresh water are separated by large-scale regionally occurring aquitards (formations with very low hydraulic conductivity), and the occurrence of fresh water is therefore often restricted to a thickness of a few 100 metres. The saltwater at greater depths does not participate in the surface-near water cycle, or only does so to a limited extent. Now, a new field of research is the evaluation of the influence of the utilization of geo-resources in deep groundwater systems (e.g. CO2 storage in saline aquifers) with regards to the hazard to fresh water resources in shallow areas. This will be a key aspect in the future for sustainable groundwater management.
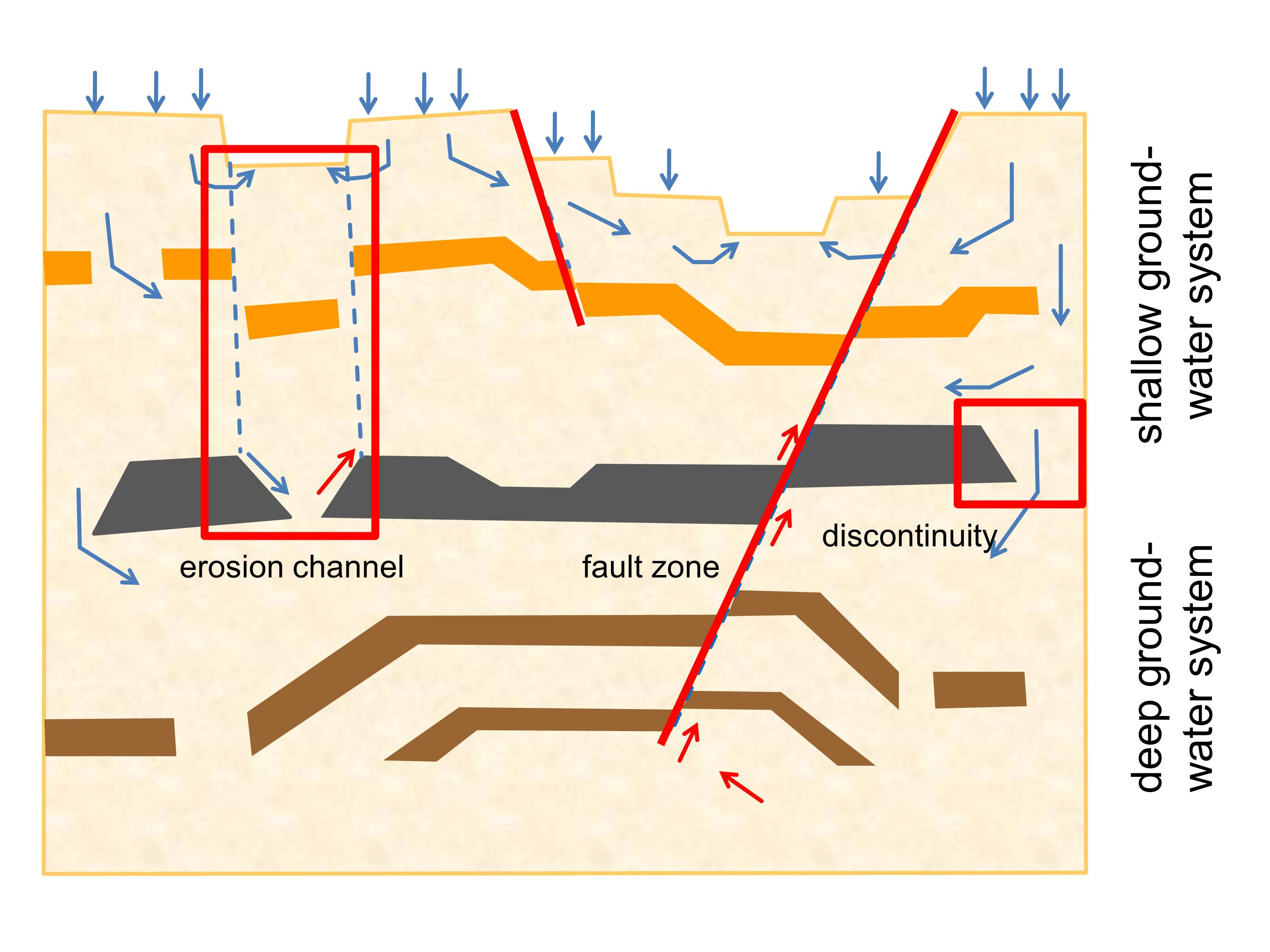
Schematic diagram showing the different groundwater systems and potential for fluid flow in the subsurface.
In the centre of my studies are ore, crude oil, natural gas and coal deposits, as well as the utilization of geothermal energy, or the storage of gas, carbon dioxide and energy. I am convinced that successful subsurface management can only be done via interdisciplinary collaboration among geology, geochemistry, geophysics, geological engineering, mineralogy, geoinformatics, drilling engineering and hydrogeology.
The multidimensional anthropogenic exploitation of the subsurface has to find solutions to the issues of technical, resource-saving, and environment-friendly feasibility, also against the background of economic analysis. Particularly the exploitation of deposits and storage locations requires a detailed economic analysis. The costs incurred in this context vary strongly, depending on the available infrastructure and the structure of the subsurface. They usually cause the major share of the total costs for such projects. Costs related to storage operations or accompanying monitoring activities are site-specific. The object of planning-related profitability analyses, which take into consideration the prevailing location factors, consists in the determination of the feasibility and the cost-effectiveness of the projects, also in the context of conflicts how to use subsurface structures.
With my major working tool – numerical process simulation – I aim at contributing with computer-based assessment and prognosis to the protection of resources and the environment. In that way I try to provide a basis for technical and economic decision-making processes, including the sustainable exploitation of georesources and the protection of others (e.g. groundwater).
