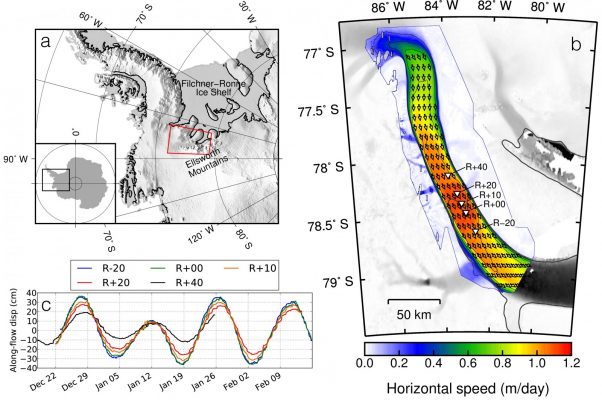
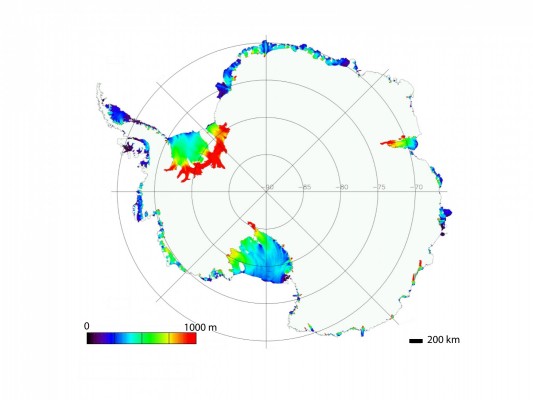
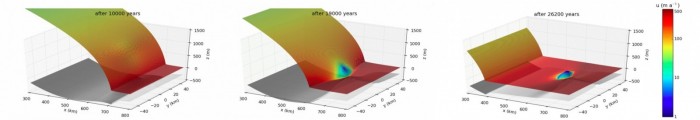
Ice streams discharge approximately 90% of the Antarctic ice onto ice shelves , and ultimately into the sea into the sea (Bamber et al., 2000; Rignot et al., 2011). Whilst flow-speed changes on annual timescales are frequently discussed, we consider here what happens on much shorter timescales! Previous studies have shown that ice streams can respond to ocean tides at distances up to 100km inland ...[Read More]
Image of the Week – How ocean tides affect ice flow