Applied mathematics is often seen as an obscure field, which the general public has no hope of ever understanding. In the context of climate science, this is far from the truth. In fact, many mathematical concepts and ideas applied to the study of the climate system stem from intuitive arguments. While their implementation can be very complex, understanding the basic ideas behind them does not req ...[Read More]
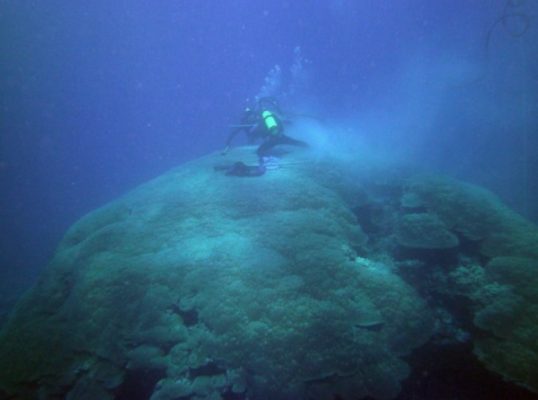
Corals, the thermometers of the past!
Name of proxy: Coral Type of record: Oceanic variability Paleoenvironment: Fringing reefs, barrier reefs, or atoll Period of time investigated: Mainly the last 200 years How does it works ? What we usually picture as a coral is actually a colony of tiny living animals called coral polyps, which are closely related to jellyfish or anemones. They live in symbiosis with photosynthetic algae called Zo ...[Read More]
Ostracods, the sentinels of past oceanic circulation
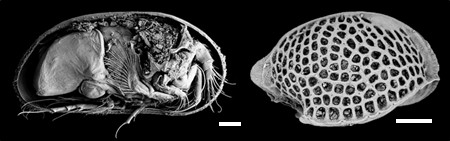
Name of the proxy Ostracoda Type of proxy Paleoenvironment proxy Paleoenvironment All types of aquatic environments but here we will focus on marine waters Period of time investigated Phanerozoic How does it work? Ostracoda are crustacean of millimetre size which have inhabited all types of marine environments from the Ordovician to today (e.g. Salas et al. 2007) and colonized continental water bo ...[Read More]
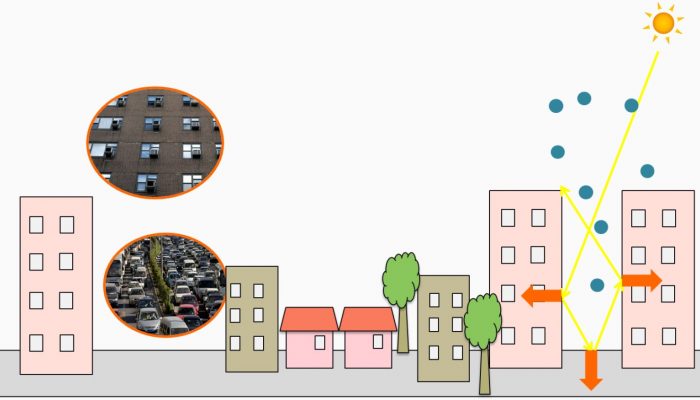
Hot towns, summer in the city!
Cities obviously experience a different climate than natural landscapes. Already in 1810 the British meteorologist Luke Howard documented that the air temperature in the city of London was several degrees higher than in its surroundings. This so called urban heat island has several causes. In general the relatively dark surfaces of asphalt and roofs absorb solar radiation very efficiently and this ...[Read More]