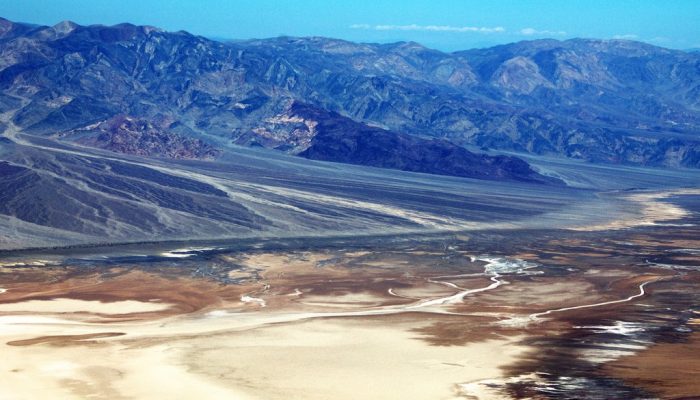
With rocks dating as far back as the Precambrian, mountain building events, violent volcanic eruptions and being covered, on and off, by shallow seas, Death Valley’s geological history is long and complex. Back in the Cenozoic (65 to 30 million years ago), following a turbulent period which saw the eruption of volcanoes (which in time would form the Sierra Nevada of California) and regional uplift ...[Read More]
Imaggeo on Mondays: Tones of sand