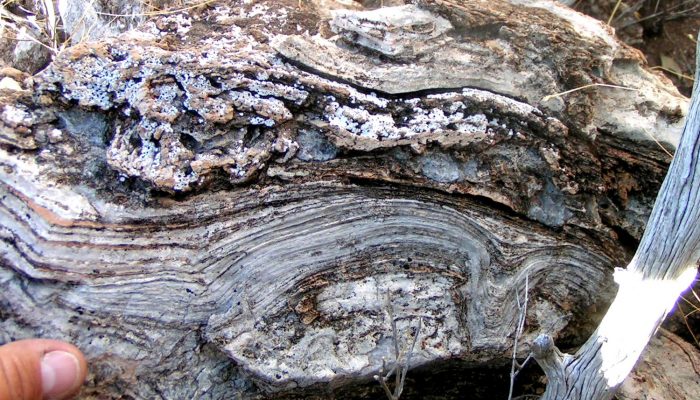
Microbialites – structures which result from the interaction between microbes and sediments – have existed in the rock record since 3700 Ma ago until the present day. The presence of microbes in environments where mineral precipitation is prevalent, usually derives in the development of such chemical sedimentary structures. This can take place in marine, non-marine, and subterranean environm ...[Read More]
Imaggeo on Mondays: The odd ‘living’ rocks