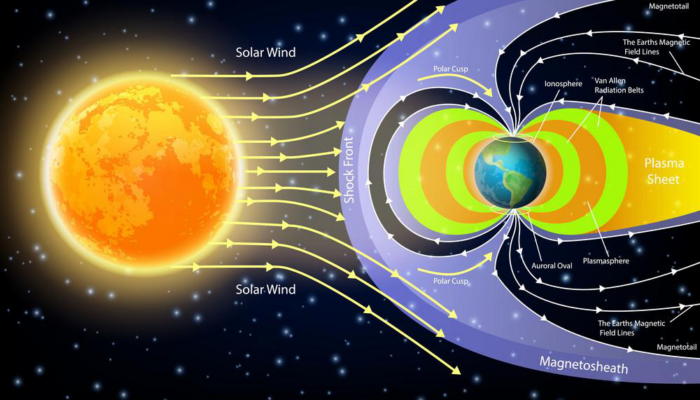
Particle Precipitation High energy particles (e.g. electrons and protons) that precipitate at high latitudes can alter the chemical composition of the atmosphere by different photochemical reactions. This mainly happens due to primary collision processes and subsequent ion and neutral-chemistry reactions. Such reactions ordered by increasing energy are, for example, excitation, photo-dissoc ...[Read More]
Cosmogenic Radionuclides – The quest of studying the solar activity of thousands of years
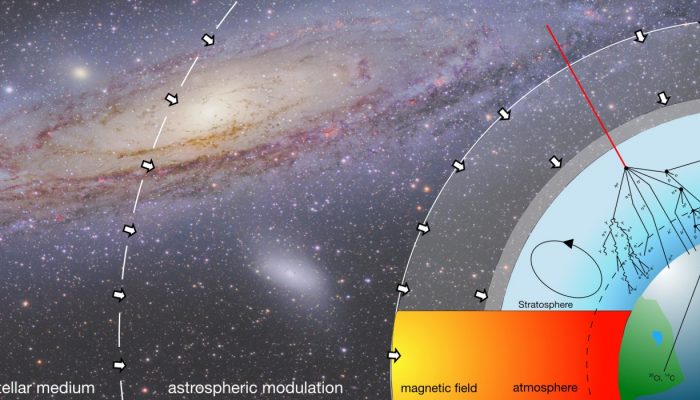
Figure 1: Sketch of the processes involved in order to model the atmospheric production of the cosmogenic radionuclides. Courtesy K. Herbst
Thanks to the invention of the Neutron Monitor in 1948 and multiple spacecraft which monitor the cosmic ray environment since 1970’s we now have a constant record of the solar activity over almost 70 years. Information prior to this space era, however, are rare and take us back in time only to the late 1930s, when ionization chambers have been introduced. This of course allows us only a narr ...[Read More]