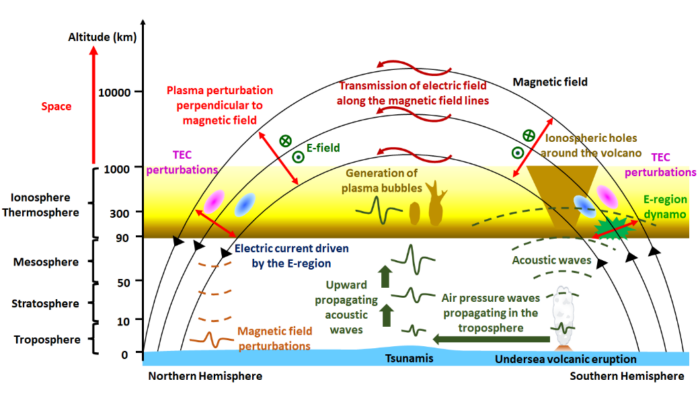
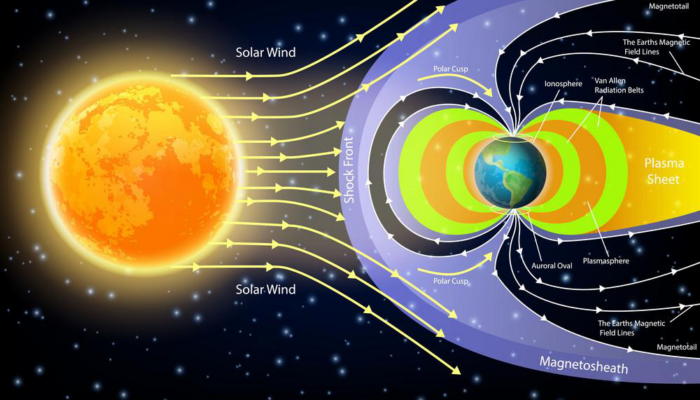
Vienna transformed into a buzzing hub of scientific exchange as the European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly (GA) 2025 took place from 27 April to 2 May. Over 20,000 scientists from 120 countries gathered to share groundbreaking research across the Earth, planetary, and space sciences. Attending the GA for the first time as part of the Early Career Scientists (ECS) Team of the Solar-Terre ...[Read More]
A Week to Remember: My EGU 2025 Experience