It’s I’m a Geoscientist week! Or more exactly: weeks. From March 9 until March 20, the EGU supports I’m a Geoscientist to help students engage with scientists about real science. The Energy, Resources and Environment Division of the European Geosciences Union encompasses a broad range of different ERE-related topics, from surface to subsurface, spanning all aspects of geosciences. In order to demonstrate how broad the Division actually is, and what you can do as a geoscientist to be involved with energy, resources or the environment, we asked the members of the ERE committee to introduce themselves and explain how their day-to-day work relates back to ERE.
After a flight through the scientific world of mining, nuclear energy, CO2 storage and groundwater flow, today we will stay above ground, with our ‘Above Ground’ Officer Viktor Bruckman, who is working at the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
***
 The European Geosciences Union (EGU) Division on Energy, Resources and the Environment (ERE) deals with some of the most important aspects for sustaining humanity. The current demographic trend of a growing world population with increasing demands of energy and resources defines a challenging task in developing policies for a sustainable future. Such frameworks need to be implemented on a sound scientific basis and the ERE division provides a forum for discussing state-of-the-art projects and results at the annual general assemblies and beyond. At the ERE division, I am responsible for the aboveground section, which includes most of the renewable sources of energy (e.g. wind power, hydropower, solar power) and other resources, such as biomass.
The European Geosciences Union (EGU) Division on Energy, Resources and the Environment (ERE) deals with some of the most important aspects for sustaining humanity. The current demographic trend of a growing world population with increasing demands of energy and resources defines a challenging task in developing policies for a sustainable future. Such frameworks need to be implemented on a sound scientific basis and the ERE division provides a forum for discussing state-of-the-art projects and results at the annual general assemblies and beyond. At the ERE division, I am responsible for the aboveground section, which includes most of the renewable sources of energy (e.g. wind power, hydropower, solar power) and other resources, such as biomass.
My own background is forestry, with a strong specialization in the areas of carbon cycling and sequestration, as well as the production of biomass. I am working for the Commission for Interdisciplinary Ecological Studies at the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) that taught me to approach problems in a holistic and interdisciplinary fashion. And these are the best lessons learned in order to serve the ERE business. Indeed, the provision of sustainable resources are a very interdisciplinary matter, specifically because it is based on interventions on land and consequently causes land use change (LUC), a term recently stressed a number of times, in particular with Climate Change.
This thought alone highlights the complexity of the topic as renewable resources are commonly seen as the potential successors of the fossil sources in order to move our society towards a development based on a solid bioeconomy. In-depth analysis, however, shows that renewables are not per se better than non-renewable sources and in some cases they are even worse. This is true even from an economical point of view, especially when internalizing all associated costs, including e.g. loss of biodiversity etc. Therefore, we need a very sound understanding on how the development of renewable sources of feedstocks and energy impacts the environment and its services, which are delivered at no financial costs to the humanity (so-called ecosystem services).
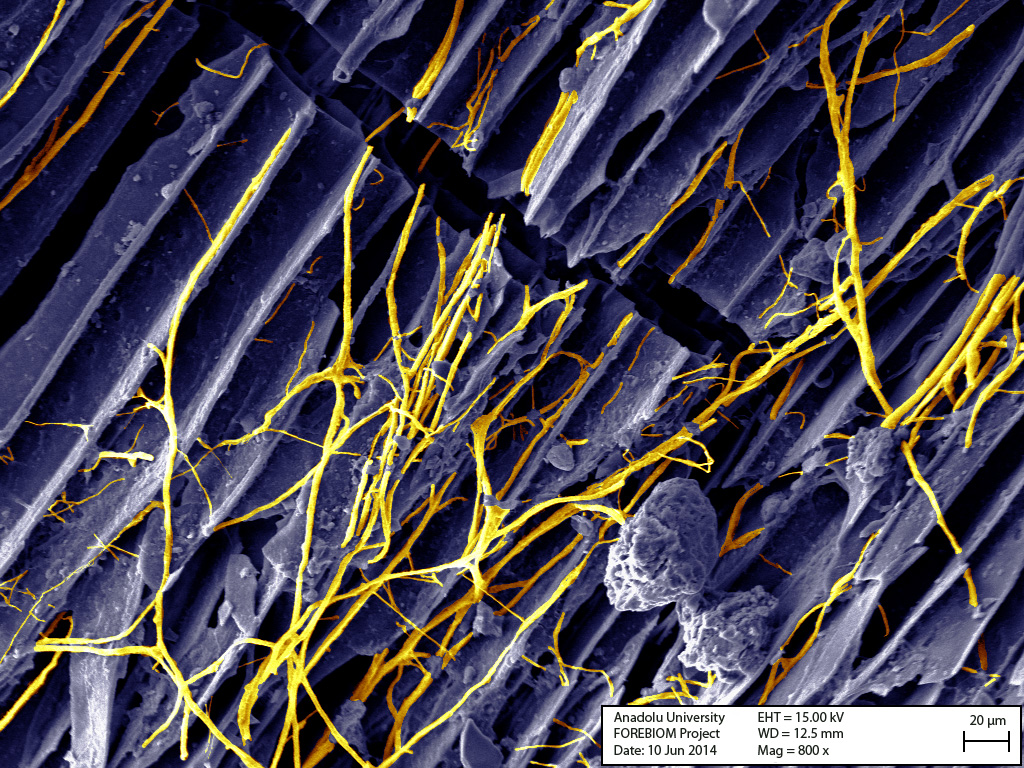
Over time, biochar particles are fully integrated into the soil system and act as a reservoir for nutrients and water as shown here by intensive occurrence of mycorrhizal hyphae (orange structures). This SEM illustration shows charcoal which was found in a spruce-dominated forest soil in the northern part of Austria and likely origins from the previously common silvicultural practice of slash burning. The age of the charcoal shown here is around 110 years, and it still shows no signs of decomposition, therefore impressively demonstrating its capabilities of securely sequestering carbon. Source: Bruckman, V.J. and Klinglmüller, M. (2014): Potentials to mitigate climate change using biochar – the Austrian perspective. IUFRO Occasional Papers (27) 1-19.
Experts agree that atmospheric CO2 emitted from anthropogenic sources plays a major role as a greenhouse gas (GHG). Biomass – and this is the point, where I would like to come back to my own research – has some interesting, but very region-specific potentials to reduce emissions or even sequester additional carbon from the atmosphere. An increased substitution of fossil with renewable resources that are produced under sustainable conditions may reduce large amounts of carbon emissions. My research team goes even further and proposed negative carbon emissions when using biomass as source for energy. This can be realized when combining biomass and CCS (carbon capture and storage), by producing biochar, for instance. Biochar is the solid, carbon-rich residue of biomass pyrolysis, the heating of biomass in an oxygen-low environment. The material is closely related to wood charcoal used for barbecue, just with a distinct different function. It is used as a soil amendment and, because of its unique porous structure and chemical composition it may enhances soil fertility while being very resistant against microbial decomposition. The positive effect may be realized as a consequence of increased nutrient- and water retention, improvement of soil structure and higher cation exchange capacities (CEC). Moreover it can serve as a habitat for soil microorganisms as well as soil fungi (mycorrhiza) that is known to support plant growth in a symbiotic relationship.
This example shows that the ERE division is indeed one of the most interdisciplinary divisions with a large number of connections within the EGU. This is also expressed by the large number of co-organized sessions with various other divisions. I personally enjoy working for ERE and thus add a small contribution of ERE’s success for the sake of science and ultimately a sustainable future.






