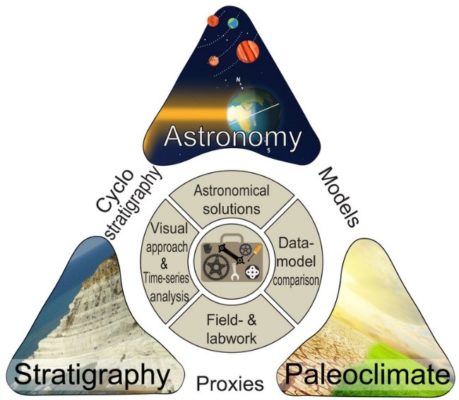
Cyclostratigraphers aim to read and understand the effect of climate-driven orbital changes in the geological record through time. In doing so, they start from an important prerequisite: An imprint of insolation variations caused by Earth’s orbital eccentricity, obliquity and/or precession (Milankovitch forcing) can be preserved in the geological rock record. The new www.cyclostratigraphy.org webs ...[Read More]
What’s my age again? Comparing dating methods in loess
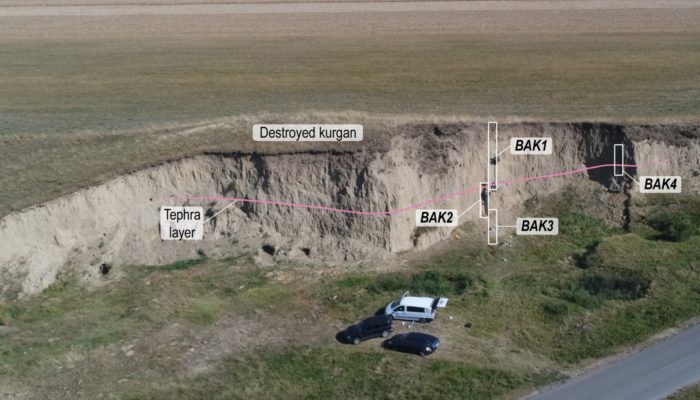

As you have learned from our previous posts, loess is a widespread terrestrial sediment, known to be an important archive for the changes of past environmental and climatic conditions. In order to use loess as a proxy, we first need to investigate the age of the sediments. In loess, different dating methods can be used, such as luminescence dating, radiocarbon dating, magnetic stratigraphy, and or ...[Read More]
Desert loess: formation, distribution, geoscientific value

Loess is an aeolian (wind-driven) silty sediment covering over 10% of the Earth’s land surface; it occurs predominantly in the mid-latitudes. On a global scale, loess is among the most widespread unconsolidated sediments, and of crucial importance for agricultural regions where loess deposits are known to form fertile soils because of its ability to store water and retain nutrients. Loess is compr ...[Read More]