When many people hear the word groundwater they imagine a raging underground torrent of water flowing along a pathway called an aquifer. Well, sorry to disappoint you, but you could not be more wrong about how groundwater exists and flows. In this post we will discuss the very basics of groundwater science (hydrogeology) and flow.
What is groundwater?
As the name implies groundwater is simply water that exists underground. It is the opposite of surface water, which exists on the surface of the Earth such as lakes, rivers and oceans. Groundwater is an extremely important resource for industry, drinking water and other applications, however, it is generally quite poorly understood. The branch of geology that researches groundwater is called hydrogeology and is still a relatively new sector of the geological sciences.
As I have already mentioned groundwater exists underground. However, there are still lots of misconceptions about how people envision groundwater. Many see large underground lakes and rivers, and while those do exist, they represent an infinitesimally small percentage of all groundwater. Generally speaking groundwater exists in the pore spaces between grains of soil and rocks. Imagine a water filled sponge. All of the holes in that sponge are water-filled. By squeezing that sponge we force the water out, similarly, by pumping an aquifer we force the water out of pore spaces.

Notice that SpongeBob is full of pore spaces…I’m not sure if they are water-filled though. (Source: Wikipedia)
There are lots of terms in hydrogeology, most of which are very simple, but essential. Here are a few of the big ones and their meanings.
Porosity: Porosity is an intrinsic property of every material. It refers to the amount of empty space within a given material. In a soil or rock the porosity (empty space) exists between the grains of minerals. In a material like gravel the grains are large and there is lots of empty space between them since they don’t fit together very well. However, in a material like a gravel, sand and clay mixture the porosity is much less as the smaller grains fill the spaces. The amount of water a material can hold is directly related to the porosity since water will try and fill the empty spaces in a material. We measure porosity by the percentage of empty space that exists within a particular porous media.
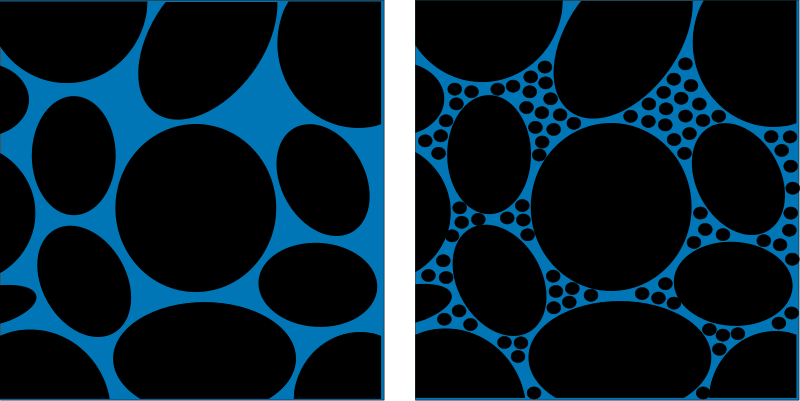
Porosity in two different media. The image on the left is analagous to gravel whereas on the right smaller particles are filling some of the pores and displacing water. Therefore, the water content of the material on the right is less. (Source: Wikipedia)
Permeability: Permeability is another intrinsic property of all materials and is closely related to porosity. Permeability refers to how connected pore spaces are to one another. If the material has high permeability than pore spaces are connected to one another allowing water to flow from one to another, however, if there is low permeability then the pore spaces are isolated and water is trapped within them. For example, in a gravel all of the pores well connected one another allowing water to flow through it, however, in a clay most of the pore spaces are blocked, meaning water cannot flow through it easily.

Video showing how connected pores have high permeability and can transport water easily. Note that some pores are isolated and cannot transport water trapped within them. (Source)
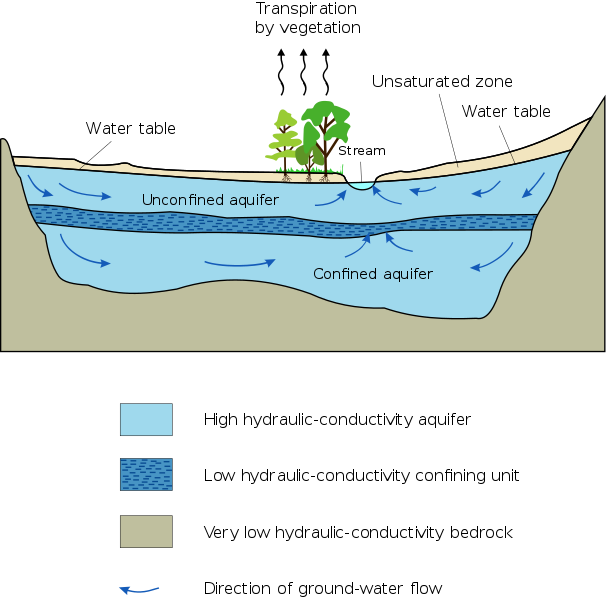
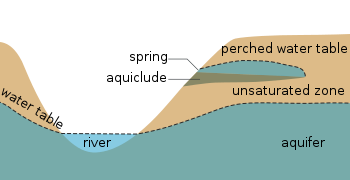
Cross section of what the water table looks like as a line. Remember it is actually a surface that extends in every direction. Note that the water in the well only rises to the surface of the water table because air pressure and water pressure are equal at the water table. (Source: Wikipedia)
Groundwater Flow
The study of hydrogeology is a very mathy one. There are lots of complicated equations, Greek letters, and funny squiggles. However, you don’t need an advanced degree in math to understand the basics, but it helps to know a little bit. Basically all ground water flow can be described by a single simple equation. Sure, there have been lots of modifications made to fit specific conditions and circumstances, but it all comes back to the same basic principles outlined in a single equation. That equation is called Darcy’s Law (cue dramatic music).
 |
| Henry Darcy – “The father of hydrogeology” |
Darcy’s law states that the velocity water flows is dependant on the material which it flows through and the hydraulic gradient, which is the difference in water level between two points of measurement divided by the distance between them. In mathematical terms it looks like this:
 |
| Darcy’s Law |
Q is the discharge or the amount of water that flows out of a given material over a set amount of time.
 |
| Graphical representation of Darcy’s Law in a hypothetical porous medium with two points of measurement (h1 and h2) and a hydraulic conductivity of K. (Matt Herod – 2011) |
So now we understand some of the basic principles governing groundwater flow, but we haven’t discussed why it would flow from one place to another. We all take it for granted that groundwater is not stationary and moves, but why is that? The answer is shockingly simple, and lies in the fact that everything in nature is in a constant struggle to find balance.
Water flows from areas of high energy to low energy in an attempt to distribute that energy evenly throughout the water table. In this case energy is not a synonym for electricity, but energy in all forms, such as pressure or concentration differences. In the case of the water table the driving force is usually differences in pressure and elevation along the surface of the water table which lead to water flow. In hydrogeological terms these energy differences are referred to as hydraulic head, which can be measured at any point in the water table. It is helpful to imagine the weather when we think of groundwater flow. We all know that wind moves from areas of high air pressure to low air pressure bringing weather changes and temperature fronts in with it. Groundwater behaves the same and moves from places with high hydraulic head to low hydraulic head the same as the wind.
Obviously there is much more to discuss in the field of hydrogeology. The big topics being this like contamination or freshwater resources. However, in order to discuss those topics properly it is crucial to have a solid grasp on groundwater terms and basics. Please feel free to to comment if you have any suggestions for future posts on groundwater. Thanks for reading.
Matt
Note: This is a re-post from my old, less visited geo-blog. It was previously posted on June 13, 2011.



