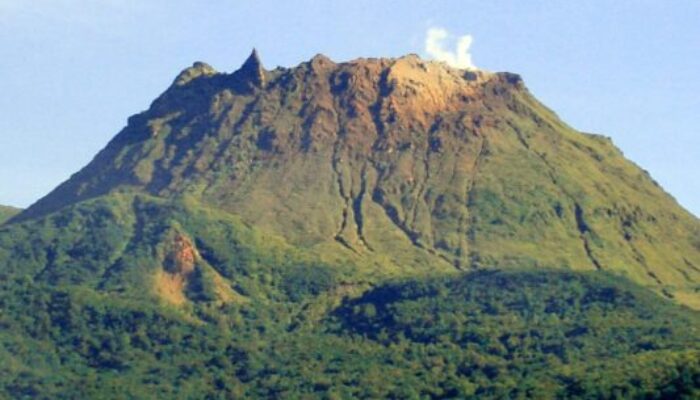
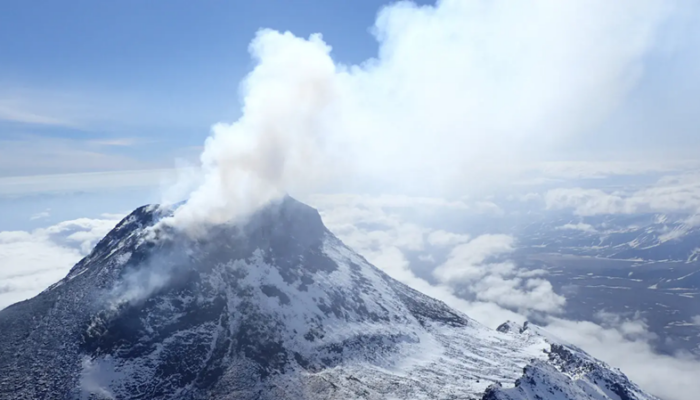
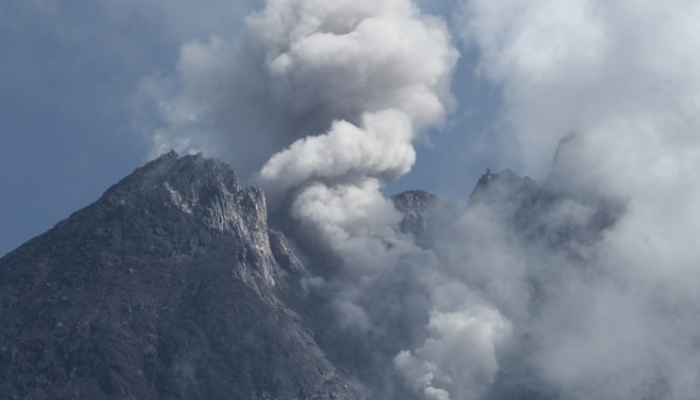
La Soufrière de Guadeloupe is an andesitic stratovolcano located in the southern part of Basse-Terre, within the Guadeloupe archipelago (Eastern Caribbean). It towers over the towns of Sainte-Claude and Basse-Terre. Nearly 50 years ago, this region faced severe consequences from a phreatomagmatic eruption, forcing the evacuation of 80,000 people. Since then, the volcano has been regularly monitore ...[Read More]
La Soufrière de Guadeloupe: Past Eruptions and Ongoing Activity