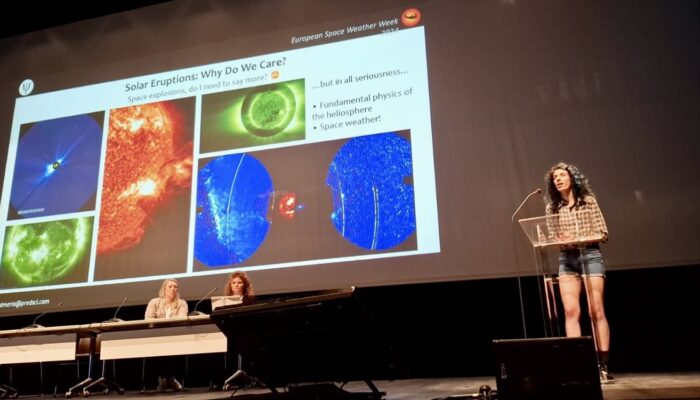
Congratulations on receiving the EGU 2024 ST Division Outstanding Early Career Scientist Award for your exceptional research in analyzing complex solar transients and their effects on space weather. What does this recognition mean to you personally, and how does it impact your work in this fascinating field? Thank you so much! Receiving an award from EGU is of particular significance to me, since ...[Read More]
If you didn't find what you was looking for try searching again.
Solar-Terrestrial Sciences
ST-Early Career Scientist team 2024-2025
We are a group of Early Career Scientists (ECSs) from the Solar-Terrestrial (ST) division, dedicated to organizing events and activities for ST-ECSs both during the EGU General Assembly and throughout the year. Our goal is to enhance ECS visibility and create valuable networking opportunities. Currently the team is formed by: Dr. Liliana Macotela, ECS Representative Liliana is a seni ...[Read More]
Cryospheric Sciences
Navigating the polar frontier: exploring the effects of sea-ice decline on shipping and sea routes in the Arctic
Sea ice is a critical part of the unique Arctic ecosystem, but climate change is becoming a serious threat. Warming in the Arctic has already resulted in the loss of over 4 million km² of sea ice. But is it all bad? Retreat of Arctic sea ice is allowing more ships to navigate the Arctic Ocean, along shorter, faster and cheaper sea routes, providing emission reductions of 24%. But will the growth o ...[Read More]
GeoLog
Congratulations to the winners of the best EGU division blogs of 2024!
If you’re a regular reader of the EGU blogs, you may notice a certain annual tradition of ours: we like to celebrate the contribution of our science writers and bloggers over the year gone by. And 2024 was no exception of course; we had a number of inspiring and thought-provoking blog posts published across the EGU’s official blog GeoLog and division blogs. Thank you to each one of you for your ti ...[Read More]
Geochemistry, Mineralogy, Petrology & Volcanology
EGU Webinar Alert! “Careers inside and outside of academia: Panel Discussion”
We are delighted to invite you to the upcoming EGU webinar, “Careers Inside and Outside of Academia: Panel Discussion,” scheduled for Tuesday, 11 March 2025, at 16:00 CET. Secure your spot by registering through the following link: Registration Link. If you are struggling to navigate the choice between academic and non-academic jobs, you are not alone. While many challenges related to ...[Read More]
Biogeosciences
Unleashing Blue Carbon: Meet the New BluECR Network
Welcome to our new blog post! Today, we’re diving into the world of Blue Carbon Ecosystems (BCEs) and introducing you to an exciting new initiative—the BluECR network. Whether you’re new to blue carbon or already working in these vital habitats, this post will provide insights into their importance and invite you to join a community dedicated to advancing blue carbon research. Climate change ...[Read More]
Geomorphology
Highlighting Chris D. Clark, the GM Division Ralph Alger Bagnold Awardee 2025
This blog post is part of our series: “Highlights” for which we’re accepting contributions! Please contact one of the GM blog editors, Emily (eb2043@cam.ac.uk) or Emma (elodes@asu.edu), if you’d like to contribute on this topic or others. Recently, EGU announced the 2025 medals and awards to be presented at the General Assembly in April, and the winner of the Geomorphology Division Ralph Alger Bag ...[Read More]
GeoLog
Geo-magicians: The mysterious work of understanding our magnetic Earth
There is a force all around us—unseen, unfelt, and yet profoundly influential. It guides the migration of birds across continents, whispers secrets to ancient rocks, and shields us from cosmic storms. This force is as mysterious as it is essential, shaping our world in ways that most of us never think about. Imagine a sailor centuries ago, staring at a compass that always points north. What guides ...[Read More]
Geodesy
Inside the World of ‘Skype a Scientist’
Let’s move onto another amazing researcher and ECS, Öykü Koç, who is involved with ‘Skype a scientist’, an educational nonprofit with a focus on connecting people with science in fun and meaningful ways, making science education available and engaging for everyone. Öykü Koç (she/they) is a PhD candidate at Politecnico di Milano (Italy), with her research focusing on the time-variable gravity field ...[Read More]
Tectonics and Structural Geology
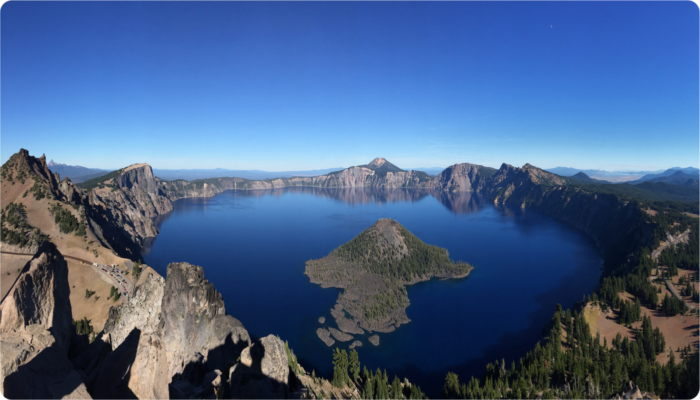
Geomythology. Crater Lake: from Love, War and/or natural phenomena
The worldwide relatively frequent recurrence of volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and tsunamis, as well as their strong impact on society make them the most common sources of myths. The most intriguing part is how different cultures describe relatively similar events in very different ways. Among them, the myths at the base of the origins of the Crater Lake in Oregon (USA), mainly orally inherited f ...[Read More]